Which social media platforms facilitate monitoring the opioid crisis?
- PMID: 40293990
- PMCID: PMC12036940
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000842
Which social media platforms facilitate monitoring the opioid crisis?
Abstract
Social media can provide real-time insight into trends in substance use, addiction, and recovery. Prior studies have used platforms such as Reddit and X (formerly Twitter), but evolving policies around data access have threatened these platforms' usability in research. We evaluate the potential of a broad set of platforms to detect emerging trends in the opioid use disorder and overdose epidemic. From these, we identified 11 high-potential platforms, for which we documented policies regulating drug-related discussion, data accessibility, geolocatability, and prior use in opioid-related studies. We quantified their volume of opioid discussion, including in informal language by including slang generated using a large language model. Beyond the most commonly used Reddit and X/Twitter, the platforms with high potential for use in opioid-related surveillance are TikTok, YouTube, and Facebook. Leveraging a variety of social platforms, instead of merely one, yields broader subpopulation representation and safeguards against reduced data access in any single platform.
Copyright: © 2025 Carpenter et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

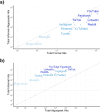
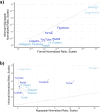
Update of
-
Which social media platforms facilitate monitoring the opioid crisis?medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 4:2024.07.06.24310035. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.06.24310035. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLOS Digit Health. 2025 Apr 28;4(4):e0000842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000842. PMID: 39006412 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Which social media platforms facilitate monitoring the opioid crisis?medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 4:2024.07.06.24310035. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.06.24310035. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLOS Digit Health. 2025 Apr 28;4(4):e0000842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000842. PMID: 39006412 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Characterizing and Identifying the Prevalence of Web-Based Misinformation Relating to Medication for Opioid Use Disorder: Machine Learning Approach.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Dec 22;23(12):e30753. doi: 10.2196/30753. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34941555 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Discussion of Telehealth in Two Social Media Platforms: Social Listening Analysis.Telemed Rep. 2023 Aug 3;4(1):236-248. doi: 10.1089/tmr.2023.0008. eCollection 2023. Telemed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37637375 Free PMC article.
-
Conspiracy theories and social media platforms.Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Oct;47:101407. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2022.101407. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35868169 Review.
-
A review of social media platform policies that address cannabis promotion, marketing and sales.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2023 Jun 19;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13011-023-00546-x. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2023. PMID: 37337216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring the opioid epidemic via social media discussions.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 May 15;8(1):284. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01642-x. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40374984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaafarani HMA, Han K, El Moheb M, Kongkaewpaisan N, Jia Z, El Hechi MW, et al.. Opioids after surgery in the United States versus the rest of the world: the International Patterns of Opioid Prescribing (iPOP) Multicenter Study. Ann Surg. 2020;272(6):879–86. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004225 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manchikanti L, Singh A. Therapeutic opioids: a ten-year perspective on the complexities and complications of the escalating use, abuse, and nonmedical use of opioids. Pain Physician. 2008;11:S63–88. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
