Emergency neurosurgical separation of pygopagus conjoined twins in a triplet pregnancy: illustrative case
- PMID: 40294523
- PMCID: PMC12036354
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE24818
Emergency neurosurgical separation of pygopagus conjoined twins in a triplet pregnancy: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Conjoined twins are a rare type of congenital malformation. The point of attachment is the primary factor used to classify conjoined twins; typically, this is front to front, with thoracopagus and omphalopagus twins accounting for about 75% of cases and pygopagus twins only between 6% and 19%.
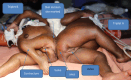
Observations: This is a case report of 46-day-old female triplets born to a 37-year-old para 4 mother. Triplets A and B were conjoined at the lumbosacrococcygeal area dorsally. Triplet C was not conjoined. The conjoined triplets had a low birth weight; hence, it was decided to start nutritional management and achieve adequate weight gain before surgical separation. While on nutritional management, at 46 days of age, triplet B developed cardiorespiratory failure. Therefore, the multidisciplinary team decided to proceed with emergency neurosurgical separation surgery, with the primary aim of saving triplet A. Triplet B died 7 hours after the surgery due to irreversible cardiorespiratory failure, and triplet A remained in the hospital for 14 days and was discharged with intact neurological function.
Lessons: Most cases of conjoined twins do not require emergency separation surgery and need nutritional support before the separation procedure. Separation surgery requires a multidisciplinary team meeting, planning ahead of time, and preparation. https://thejns.org/doi/10.3171/CASE24818.
Keywords: conjoined twins; malformation; neurosurgical; pygopagus; separation; triplets.
Figures



References
-
- Jain P Kundal AK Sharma R Khilnani P Kumar P Kumar P.. Surgical separation of pygopagus twins: a case report. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2014;2(3):119-122.
-
- Hirokazu T Takayuki I Yoshinori H Kazunari K Akio A Keiji K.. Separation surgery of pygopagus asymmetrical conjoined twins sharing U-shaped spinal cord: case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29(4):699-706. - PubMed
-
- Sabeh-Ayoun K Al Tahan H Akel S Zaghal A.. Successful separation of pygopagus conjoined twins: a case report. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2023;99.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

