First Experiences of Pilot Clinical Studies on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Recurrent Gastrointestinal Cancers Using an Intravenous Injection of 10BPA
- PMID: 40294997
- PMCID: PMC12041971
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13948
First Experiences of Pilot Clinical Studies on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Recurrent Gastrointestinal Cancers Using an Intravenous Injection of 10BPA
Abstract
Background/aim: Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a novel treatment that induces targeted tumor cell damage through the selective accumulation of 10B compounds in cancer cells followed by the production of alpha and lithium particles using thermal neutron irradiation. Despite its potential, clinical applications of BNCT for recurrent gastrointestinal cancers remain limited. This study presents the first pilot clinical evaluation of BNCT using intravenous boronophenylalanine (10BPA) for such cancers.
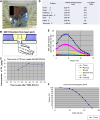
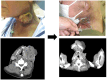
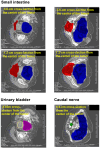
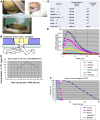
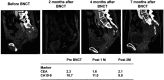
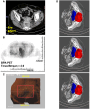
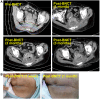
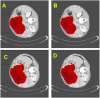
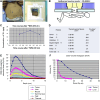
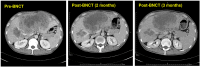
Case reports: Four patients with recurrent gastrointestinal cancers were enrolled in this phase I-II clinical study. All had tumors refractory to standard treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. BNCT was performed using thermal neutron irradiation at Kyoto University Research Reactor. 10BPA was administered intravenously at 400 mg/kg, and no severe adverse effects were observed. Tumor responses varied, with one patient achieving partial response and three demonstrating stable disease at three months post-treatment. Notably, BNCT alleviated cancer-related symptoms, such as pain and nerve compression, improving patients' quality of life. Dosimetric evaluations confirmed effective tumor doses with acceptable exposure to surrounding normal tissues.
Conclusion: BNCT is a promising modality for recurrent gastrointestinal cancers, offering symptom relief and potential antitumor effects. Its safety and feasibility were demonstrated in this study. Future research should explore fractionated BNCT and combination therapies with immunotherapy or targeted agents to enhance efficacy further.
Keywords: Alpha particle; Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT); Boronophenylalanine (10BPA); atomic reactor; recurrent gastrointestinal cancers; thermal neutron.
Copyright © 2025, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this study.
Figures




References
-
- Locher GL. Biological effects and therapeutic possibilities of neutrons. Am J Roentgenol. 1936;36:1–13.
-
- Kageji T, Nagahiro S, Kitamura K, Nakagawa Y, Hatanaka H, Haritz D, Grochulla F, Haselsberger K, Gabel D. Optimal timing of neutron irradiation for boron neutron capture therapy after intravenous infusion of sodium borocaptate in patients with glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(01)01605-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
