Nivolumab and stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with breast cancer brain metastases: long-term results and biomarker analysis from a non-randomized, open-label, phase Ib study
- PMID: 40295143
- PMCID: PMC12039042
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-011432
Nivolumab and stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with breast cancer brain metastases: long-term results and biomarker analysis from a non-randomized, open-label, phase Ib study
Abstract
Background: We hypothesized treatment with nivolumab and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) would be feasible, well tolerated, and may improve intracranial tumor control over SRS alone for breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM).
Methods: The study is a phase Ib trial of nivolumab and SRS for BCBM.
Clinical trial information: NCT03807765. Key eligibility criteria include BCBM of all subtypes, age ≥18, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performace Status (ECOG-PS)≤2 with ≤10 brain metastases. Treatment was initiated with a dose of nivolumab (480 mg intravenously) that was repeated every 4 weeks. The initial dose of nivolumab was followed 1 week later by SRS. Blood was collected at baseline and every 4 weeks for flow cytometry and cell-free DNA (cfDNA) assessment.
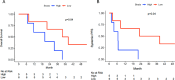
Results: A total of 12 patients received SRS to 17 brain metastases. Breast cancer subtypes included triple negative (50%), hormone receptor (HR)+/HER2- (33%), and HR-/HER2+ (17%). Median follow-up from start of protocol therapy is 56 months. No cases of radionecrosis were noted. Two lesions were noted to undergo local failure, both pathologically confirmed, for a 12-month local control of 94%. Median distant intracranial control was 7.4 months with a 12-month control rate of 33%. Median systemic progression-free survival was 7.7 months with a 12-month rate of 42%. Median overall survival (OS) was 24.7 months with a 12-month OS of 75%. Most patients were noted to have an increase in cfDNA throughout study treatment, at week 5 compared with baseline (83%), week 25 compared with baseline (89%), and 100% at first follow-up. Intracranial control was associated with lower levels of CD4 regulatory T cells (Treg) (p=0.03) and higher levels of CD4 T effector memory (p=0.04).
Conclusions: Nivolumab and SRS is a safe and feasible treatment option in BCBM. Long-term follow-up revealed no cases of radiation necrosis.
Trial registration number: NCT03807765.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; Immunotherapy; Nivolumab; Radiotherapy/radioimmunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Related to the current work: KA reports research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Outside of the current work: H-HMY has received speaker’s honoraria from BrainLab and is on the advisory boards of Novocure and AbbVie. HS serves as a consultant for AstraZeneca, Celgene, Novartis, PUMA, and Eisai. BJC has intellectual property on a HER2 dendritic cell vaccine. PF has received research funding from Pfizer and Celgene and is on the advisory boards of Novocure, BTG, Inovio, AbbVie, Ziopharm, Tocagen, and Pfizer. HSH declares that she has received a speaker’s honorarium from Lilly Pharmaceuticals, research funding to the institution from Arvinas, AbbVie, GSK, Marker therapeutics, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, SeattleGenetics, Prescient, Horizon, Zymeworks and Karyopharm. KA has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Genentech. JJC has received research funding, consulting fees, and honoraria from Varian Medical Systems. SK has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and AstraZeneca. RLBC has received consulting honoraria from Bristol-Meyers Squibb. AES has received a speaker’s honorarium from Lilly Pharmaceuticals and serves as consultant for Novartis and GE Healthcare.
Figures


References
-
- Nanda R, Liu MC, Yau C, et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab Plus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Pathologic Complete Response in Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: An Analysis of the Ongoing Phase 2 Adaptively Randomized I-SPY2 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:676–84. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
