The Diagnosis and Therapy of XLH
- PMID: 40295317
- PMCID: PMC12037658
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-025-01374-w
The Diagnosis and Therapy of XLH
Abstract
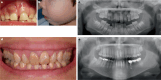
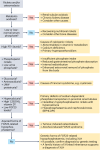
X-linked hypophosphatemia is a rare genetic disease caused by pathogenic variants in the PHEX (phosphate-regulating endopeptidase homolog X-linked) gene with X-linked dominant inheritance that causes metabolic bone disease and other severe complications. PHEX dysfunction results in increased production and secretion of the phosphaturic hormone fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) from bone. The consequences of FGF23 excess are renal phosphate wasting and decreased calcitriol synthesis, leading to hypophosphatemia and subsequently rickets and osteomalacia. Children with XLH usually become symptomatic in the second year of life presenting with progressive disproportionate short stature, bone pain, frontal bossing, enlarged joints, bowed legs, and a waddling gait. Various other symptoms may develop later, including dental abscesses, peritonitis, hearing loss, pseudofractures, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, and enthesopathies, often leading to a diminished quality of life and ultimately disability. Here, we provide an overview of the current knowledge of the pathophysiology and treatment insights of this rare and challenging disease, including the targeting of FGF23 as a therapeutic approach that has significantly improved patient outcomes.
Keywords: Burosumab; FGF23; Osteomalacia; Phosphate; Rickets; XLH.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Dieter Haffner received speaker fees, consultation fees, and research grants from Kyowa Kirin. Ineke Böckmann declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beck-Nielsen SS, Brock-Jacobsen B, Gram J, Brixen K, Jensen TK (2009) Incidence and prevalence of nutritional and hereditary rickets in southern Denmark. Eur J Endocrinol 160(3):491–7. 10.1530/eje-08-0818 - PubMed
-
- Endo I, Fukumoto S, Ozono K, Namba N, Inoue D, Okazaki R et al (2015) Nationwide survey of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23)-related hypophosphatemic diseases in Japan: prevalence, biochemical data and treatment. Endocr J 62(9):811–6. 10.1507/endocrj.ej15-0275 - PubMed
-
- Kamenický P, Briot K, Munns CF, Linglart A (2024) X-linked hypophosphataemia. Lancet 404(10455):887–901. 10.1016/s0140-6736(24)01305-9 - PubMed
-
- Trombetti A, Al-Daghri N, Brandi ML, Cannata-Andía JB, Cavalier E, Chandran M et al (2022) Interdisciplinary management of FGF23-related phosphate wasting syndromes: a Consensus Statement on the evaluation, diagnosis and care of patients with X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol 18(6):366–84. 10.1038/s41574-022-00662-x - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

