An anti-virulence drug targeting the evolvability protein Mfd protects against infections with antimicrobial resistant ESKAPE pathogens
- PMID: 40295486
- PMCID: PMC12037726
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58282-8
An anti-virulence drug targeting the evolvability protein Mfd protects against infections with antimicrobial resistant ESKAPE pathogens
Abstract
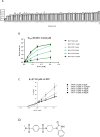
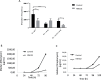
The increasing incidence of antibiotic resistance and the decline in the discovery of novel antibiotics have resulted in a global health crisis, particularly, for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, for which therapeutic dead-ends are alarming. Here, we identify and characterize a molecule, NM102, that displays antimicrobial activity exclusively in the context of infection. NM102 inhibits the activity of the non-essential Mutation Frequency Decline (Mfd) protein by competing with ATP binding to its active site. Inhibition of Mfd by NM102 sensitizes pathogenic bacteria to the host immune response and blocks infections caused by the clinically-relevant bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, without inducing host toxicity. Finally, NM102 inhibits the mutation and evolvability function of Mfd, thus reducing the bacterial capacity to develop antimicrobial resistance. These data provide a potential roadmap for the development of drugs to combat antimicrobial resistance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.T., N.R., and D.R. declare the following competing interests: a patent application (EP3868376, 2021) has been published, describing the use of NM102 and its derivatives as antibiotics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Cook, M. A. & Wright, G. D. The past, present, and future of antibiotics. Sci. Transl. Med.14, eabo7793 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Butler, M., Blaskovich, M. & Cooper, M. Antibiotics in the clinical pipeline at the end of 2015. J. Antibiot.70, 3–24 (2017). - PubMed
-
- McKeage, K. Finafloxacin: first global approval. Drugs75, 687–693 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

