Comparing the effectiveness of an e-learning module at different levels of magnification for detecting occlusal caries in permanent teeth, utilizing the international caries detection and assessment system (ICDAS): an ex vivo study
- PMID: 40295493
- PMCID: PMC12037830
- DOI: 10.1038/s41405-025-00323-x
Comparing the effectiveness of an e-learning module at different levels of magnification for detecting occlusal caries in permanent teeth, utilizing the international caries detection and assessment system (ICDAS): an ex vivo study
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare the effectiveness of low and high magnifications in detecting occlusal caries in permanent posterior teeth using the International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS) II criteria through the ICDAS e-learning program.
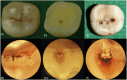
Materials and methods: Forty extracted permanent posterior teeth were used. Two examiners received e-learning training on the ICDAS webpage for detecting occlusal caries before visual examinations. Visual inspections were performed under ×2.5 magnification with a magnifying loupe and ×25 magnification with a dental surgical microscope within a week. The ICDAS scores assigned by both examiners were validated by an ICDAS expert. The visual assessment results were compared with the histological analysis results using Downer's criteria as the gold standard.
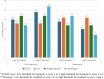
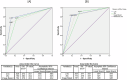
Results: Inter-examiner reliability for ICDAS-II scoring at low magnification (×2.5 loupe) and high magnification (×25 operating microscope) was moderate. However, the lenient (binary) criteria showed substantial agreement at both magnifications. Specificity was highest for both the low and high treatment thresholds (88.2% and 81.5%, respectively) at low magnification, whereas sensitivity peaked at high magnification for the high treatment threshold criterion (91.7%). Image-based ICDAS scoring by an expert also demonstrated good diagnostic accuracy (76.9%), though it was not superior to ICDAS scoring performed under ×2.5 magnification (82.1%).
Conclusion: The ICDAS-II score, particularly the lenient criterion, demonstrated a strong correlation with histological depth. The e-learning program effectively equips dentists with diagnostic skills. Extreme magnification resulted in the overestimation of dental caries, whereas low magnification (2.5x) resulted in greater diagnostic accuracy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: There are no conflicts of interest. Institutional Ethical Committee, Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Mangalore, clearance obtained (Ref. no. MCODS/15120). Consent to participate was not required for this study, as it was an ex vivo study. Permission to use extracted teeth was obtained from the Institutional Ethical Committee of Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Mangalore, India.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Reliability and Validity of International Caries Detection and Assessment System II Coding for Occlusal Caries using Magnification.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023 Sep;16(Suppl 2):138-141. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2584. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 38078031 Free PMC article.
-
Optical magnification has no benefits on the detection of occlusal caries lesions in permanent molars using different visual scoring systems: An in vitro study.J Clin Exp Dent. 2020 May 1;12(5):e479-e487. doi: 10.4317/jced.56445. eCollection 2020 May. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020. PMID: 32509231 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of different magnification levels on visual caries detection with ICDAS.J Dent. 2015 Dec;43(12):1559-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 11. J Dent. 2015. PMID: 26366524
-
Detection Methods for Early Caries Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Caries Res. 2021;55(4):247-259. doi: 10.1159/000516084. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Caries Res. 2021. PMID: 34130279
-
Visual or visual-tactile examination to detect and inform the diagnosis of enamel caries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 14;6(6):CD014546. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014546. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34124773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marczuk-Kolada G, Luczaj-Cepowicz E, Obidzinska M, Rozycki J. Performance of ICDAS II and fluorescence methods on detection of occlusal caries-An ex vivo study. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2020;29:101609. - PubMed
-
- Luczaj-Cepowicz E, Marczuk-Kolada G, Obidzinska M, Sidun J. Diagnostic validity of the use of ICDAS II and DIAGNOdent pen verified by micro-computed tomography for the detection of occlusal caries lesions-an in vitro evaluation. Lasers Med Sci. 2019;34:1655–63. - PubMed
-
- Novaes TF, Matos R, Gimenez T, Braga MM, DE Benedetto MS, Mendes FM. Performance of fluorescence-based and conventional methods of occlusal caries detection in primary molars - an in vitro study. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2012;22:459–66. - PubMed
-
- Diniz MB, Rodrigues JA, Hug I, Cordeiro Rde C, Lussi A. Reproducibility and accuracy of the ICDAS-II for occlusal caries detection. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2009;37:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Neuhaus KW, Jost F, Perrin P, Lussi A. Impact of different magnification levels on visual caries detection with ICDAS. J Dent. 2015;43:1559–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

