Sodium butyrate promotes synthesis of testosterone and meiosis of hyperuricemic male mice
- PMID: 40295597
- PMCID: PMC12037722
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95846-6
Sodium butyrate promotes synthesis of testosterone and meiosis of hyperuricemic male mice
Abstract
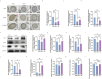
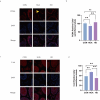
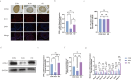
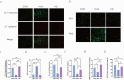
Hyperuricemia (HUA) impaires spermatogenesis. This study was carried out, aiming to determine whether butyric acid (NaB) avoids the HUA-induced decline of sperm quality HUA mice were developed through intra-peritoneal injection of the potassium oxalate combined with intragastric uric acid (UA) and by tube feeding 300 mg·kg-1·d-1NaB. The effect of NaB on the reproduction of HUA male mice was determined by measuring sperm count, sperm motility and testosterone content. In addition, TM3 and GC-2 cells were treated with a solution containing 30 mg/dl UA and 1mM NaB. The effects of NaB on the sperm quality were evaluated with the expression level of the genes involving in LH/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway and meiosis, and that encoding OPRL1 receptor protein. Results showed that NaB improved sperm count, sperm motility, testosterone synthesis, and impaired spermatocyte meiosis via HUA. In addition, in vitro analysis showed that NaB activated the LH/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway of TM3 cells, promoted the synthesis of testosterone, up-regulated the content of pain-sensitive peptide receptor (OPRL1) on the surface of GC-2 cells, and promoted meiosis. NaB also promoted the utilization of ATP by GC-2 cells. We illustrated a close relationship between HUA and spermatogenesis defects. NaB-promoted the expression of the genes functioning in testis meiosis, and the testosterone content may aid to improving spermatogenesis quality.
Keywords: Hyperuricemia; Meiosis; Sodium butyrate; Sperm quality; Testosterone.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: Animal research was approved by the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University (Approval code: AHQU-MAL20230322) and was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81671625 and 81100554/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- BS2012YY003/Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
- 2011QZ007 and 2016WS0259/Scientific and Technical Development Project of the Department of Health of Shandong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

