A U shaped association between the HCT-ALB and hospital mortality in patients with sepsis
- PMID: 40295614
- PMCID: PMC12037865
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99459-x
A U shaped association between the HCT-ALB and hospital mortality in patients with sepsis
Abstract
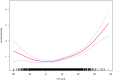
The difference between hematocrit and serum albumin (HCT-ALB) demonstrates diagnostic significance in infectious diseases, yet the nonlinear relationship between HCT-ALB and hospital mortality in ICU patients with sepsis remains unexplored. This retrospective multicenter cohort study analyzed 7,546 ICU sepsis patients (mean age 66 ± 16 years) to elucidate the HCT-ALB-mortality relationship. Using Cox proportional hazards models with smooth curve fitting, we identified a U-shaped association: Threshold analysis revealed an inflection point at 6.1. Below this threshold, each unit HCT-ALB increase corresponded to reduced mortality risk (adjusted HR 0.986, 95%CI 0.972-0.999; P = 0.036). Conversely, values ≥ 6.1 predicted escalating risk (adjusted HR 1.048 per unit increase, 95%CI 1.037-1.060; P < 0.0001). Significant age interaction was observed (P for interaction < 0.05), with heightened mortality risk in elderly patients (≥ 65 years: HR 1.022, 95%CI 1.014-1.031). These findings establish HCT-ALB as a non-linear predictor of sepsis outcomes, emphasizing its critical threshold dynamics and age-dependent prognostic implications.
Keywords: HCT-ALB; Mortality; Sepsis; U-shaped association; eICU.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between hematocrit and serum albumin levels difference and mortality in elderly sepsis patients in intensive care units-a retrospective study based on two large database.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):629. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07609-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35850582 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of plasma heparin-binding protein combined with albumin for 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Dec;36(12):1233-1237. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240718-00614. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39780664 Chinese.
-
Difference in hematocrit and plasma albumin levels as an early biomarker of severity and prognosis in patients with severe fever and thrombocytopenia syndrome.J Med Virol. 2024 Oct;96(10):e29941. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29941. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39350626
-
Association between D-dimer-to-albumin ratio and 28-days all-cause mortality in patients with sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79911-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550487 Free PMC article.
-
[The difference between hematocrit and plasma albumin in the course of systemic capillary leak syndrome: a systematic review].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Oct;30(10):920-924. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.010.002. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30439308 Chinese.
References
-
- Gotts, J. E. & Matthay, M. A. Sepsis: pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ353, i1585 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Torio, C. M. & Moore, B. J. National inpatient hospital costs: The most expensive conditions by payer, 2013. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Rockville (MD) (2006). - PubMed
-
- Liu, V. et al. Hospital deaths in patients with sepsis from 2 independent cohorts. JAMA312 (1), 90–92 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

