Quantification of intra-amniotic inflammation in late preterm prelabour rupture of membranes
- PMID: 40295647
- PMCID: PMC12038036
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99969-8
Quantification of intra-amniotic inflammation in late preterm prelabour rupture of membranes
Abstract
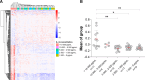
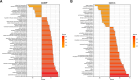
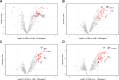
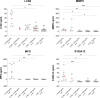
Preterm prelabour rupture of membranes (PPROM) complicated by intra-amniotic inflammation (IAI) represents a substantial proportion of preterm birth cases. Currently, IAI is frequently defined as amniotic fluid IL-6 concentration above 2,600 pg/mL. However, the amniotic fluid IL-6 concentration was never correlated with the global response of other proinflammatory proteins to the ongoing IAI. In this cross-sectional study, protein quantification was performed using mass spectrometry (MS) analysis followed by target quantification of selected proinflammatory proteins. Levels of amniotic fluid proteins determined by MS were put into the correlation with IL-6 concentration determined by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay method (ECLIA). In total, 925 proteins were efficiently quantified and differential expression analysis revealed 378 proteins upregulated towards IL-6 concentration above 10,000 pg/mL. Four proteins (LCN2, MMP8, MPO, and S100A12) were selected to verify the achieved results and IL-6 concentration of 10,000 pg/mL was determined as the cut-off value for global IAI response.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 measured using the automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay method for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020 Jun;33(11):1919-1926. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1533947. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020. PMID: 30293462
-
Maternal Plasma and Amniotic Fluid LBP, Pentraxin 3, Resistin, and IGFBP-3: Biomarkers of Microbial Invasion of Amniotic Cavity and/or Intra-amniotic Inflammation in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Nov 15;36(44):e279. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e279. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34783213 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical fluid interleukin 6 and intra-amniotic complications of preterm prelabor rupture of membranes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018 Apr;31(7):827-836. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2017.1297792. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018. PMID: 28277919
-
Amniotic fluid clusterin in pregnancies complicated by the preterm prelabor rupture of membranes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017 Nov;30(21):2529-2537. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2016.1255192. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017. PMID: 27806672
-
Amniotic fluid cell-free DNA in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes.Prenat Diagn. 2018 Dec;38(13):1086-1095. doi: 10.1002/pd.5366. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Prenat Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30276834
References
-
- Mercer, B. M. Preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Obstet. Gynecol.101 (1), 178 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Mercer, B. M. Preterm premature rupture of the membranes: current approaches to evaluation and management. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin.32 (3), 411–428 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Kacerovsky, M. et al. Prelabor rupture of membranes between 34 and 37 weeks: the intraamniotic inflammatory response and neonatal outcomes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.210 (4), 325e1–325e10 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Rose, R. & Engle, W. A. Optimizing care and outcomes for late preterm neonates. Curr. Treat. Options Peds. 3 (1), 32–43 (2017).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

