Identification of QTLs associated with grain yield-related traits of spring barley
- PMID: 40295941
- PMCID: PMC12038964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06588-6
Identification of QTLs associated with grain yield-related traits of spring barley
Abstract
Background: Numerous quantitative trait loci (QTLs) and candidate genes associated with yield-related traits have been identified in barley by genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis. However, genetic bottlenecks in elite cultivars have reduced diversity, limiting further yield improvements. Grain yield is a complex, polygenic trait shaped by genetic and environmental factors, necessitating integrative breeding approaches. While genomic selection, marker-assisted selection, and GWAS have identified key loci for yield-related traits, functional validation remains a significant challenge.
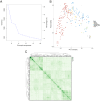
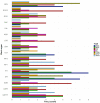
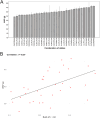
Results: A total of 346 QTLs for seven barley yield-related traits were identified in GWAS, including 93 stable QTLs across multiple environments. Two major-effect QTLs for spike length and thousand kernel weight, along with several moderate-effect QTLs, show potential for breeding. Candidate gene analysis revealed 134 highly expressed genes linked to stress response, transport, and metabolism. Notable genes include HORVU.MOREX.r3.5HG0514790 (growth and stress adaptation) and HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0212810 (seed storage protein). A total of eight presumably novel QTLs were identified. One of the novel QTLs, Hv_TKW_3H.5, had the strongest effect on total barley grain yield. The integration of favorable alleles from eight moderate- and major-effect QTLs significantly influenced the weight of kernels per spike.
Conclusions: This study aimed to identify and characterize QTLs associated with barley yield-related traits through GWAS. Integrating genomic and transcriptomic methods suggests a promising strategy for genomic selection and marker-assisted breeding to enhance barley grain yield.
Keywords: Candidate genes; Expression; GWAS; Gene combinations; SNP; Transcriptome analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- FAO. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://www.fao.org/home/en/ (2023). Accessed 20 Jan 2025.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

