Immunity in neuromodulation: probing neural and immune pathways in brain disorders
- PMID: 40296049
- PMCID: PMC12038965
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03440-4
Immunity in neuromodulation: probing neural and immune pathways in brain disorders
Abstract
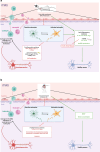
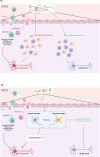
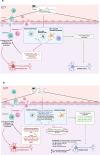
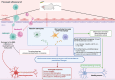
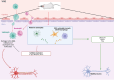
Immunity finely regulates brain function. It is directly involved in the pathological processes of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease, post-stroke conditions, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and psychiatric disorders (mood disorders, major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, psychosis disorders and schizophrenia, and neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD)). Neuromodulation is currently a leading therapeutic strategy for the treatment of these disorders, but little is yet known about its immune impact on neuronal function and its precise beneficial or harmful consequences. We review relevant clinical and preclinical studies and identify several specific immune modifications. These data not only provide insights into how neuromodulation acts to optimize immune-brain interactions, but also pave the way for a better understanding of these interactions in pathological processes.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Cytokines; Glial cells; Immunity; NDD; Neuromodulation; Parkinson disease; Post-stroke; Psychiatric disorders; Traumatic brain injury; Vascular unit.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Amanollahi M, Jameie M, Heidari A, Rezaei N. The dialogue between neuroinflammation and adult neurogenesis: mechanisms involved and alterations in neurological diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(2):923–59. 10.1007/s12035-022-03102-z. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

