Temperature and precipitation explain variation in metabolic rate but not frequency of gas exchange in Fijian bees
- PMID: 40296756
- PMCID: PMC12148022
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.249948
Temperature and precipitation explain variation in metabolic rate but not frequency of gas exchange in Fijian bees
Abstract
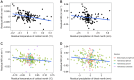
Temperature and water availability are hypothesised to be important drivers of the evolution of metabolic rate and gas exchange patterns, respectively. Specifically, the metabolic cold adaptation (MCA) hypothesis predicts that cold environments select for faster temperature-specific metabolic rates to counter the thermodynamics of biochemical reactions, while the hygric hypothesis predicts that dry environments select for discontinuous gas exchange to reduce water loss. Although these two hypotheses consider different physiological traits and how they vary along different abiotic gradients, metabolic rate drives the frequency of gas exchange in insects meaning these two traits are inherently linked. Despite this link, the MCA and hygric hypotheses are rarely considered together and the extent to which metabolic rates and frequency of gas exchange vary and co-vary across climatic gradients remains unclear. We tested the MCA and hygric hypotheses within a species of endemic Fijian bee, Homalictus fijiensis, and among four Fijian bee species across an altitudinal gradient of 1100 m (highlands are colder and wetter than lowlands). We found an MCA-like pattern within H. fijiensis and among Fijian bee species, where bees from colder environments had higher metabolic rates than bees from warmer environments when measured at 25°C, but precipitation also explained variation in metabolic rate. However, we did not find support for the hygric hypothesis within H. fijiensis or among species (frequency of gas exchange was not negatively correlated with precipitation). The relationship between metabolic rate and frequency of gas exchange was steeper for species that occupied lower elevations on average, suggesting it is possible that these two traits can evolve independently of each other despite being positively correlated.
Keywords: Discontinuous gas exchange; Evolutionary physiology; Functional traits; Hygric hypothesis; Krogh's rule; Metabolic cold adaptation; Respiration; Thermal performance; Tropical insects.
© 2025. Published by The Company of Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Addo-Bediako, A., Chown, S. L. and Gaston, K. J. (2002). Metabolic cold adaptation in insects: a large-scale perspective. Funct. Ecol. 16, 332-338. 10.1046/j.1365-2435.2002.00634.x - DOI
-
- Alton, L. A., Kutz, T., Bywater, C. L., Lombardi, E., Cockerell, F. E., Layh, S., Winwood-Smith, H., Arnold, P. A., Beaman, J. E., Walter, G. M.et al. (2024). Temperature and nutrition do not interact to shape the evolution of metabolic rate. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 379, 20220484. 10.1098/rstb.2022.0484 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beekman, M. and Van Stratum, P. (1999). Respiration in bumblebee queens: effect of life phase on the discontinuous ventilation cycle. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 92, 295-298. 10.1046/j.1570-7458.1999.00550.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

