Explore potential immune-related targets of leeches in the treatment of type 2 diabetes based on network pharmacology and machine learning
- PMID: 40296871
- PMCID: PMC12036332
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1554622
Explore potential immune-related targets of leeches in the treatment of type 2 diabetes based on network pharmacology and machine learning
Abstract
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder that poses a significant global health burden due to its profound effects on systemic physiological homeostasis. Without timely intervention, the disease can progress insidiously, leading to multisystem complications such as cardiovascular, renal, and neuropathic pathologies. Consequently, pharmacological intervention becomes crucial in managing the condition. Leeches have been traditionally used in Chinese medicine for their potential to inhibit the progression of T2DM and its associated complications; however, the specific mechanisms underlying their action and target pathways remain poorly understood. The objective of this study was to predict potential therapeutic targets of leeches in the treatment of T2DM.
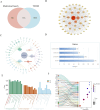
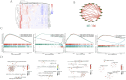
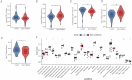
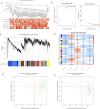
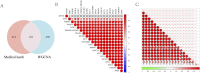
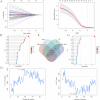
Methods: We collected active components and targets associated with leeches from four online databases, while disease-related targets were sourced from the GeneCards and OMIM databases. Following this, we performed Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis. Gene expression data were obtained from the GSE184050 dataset. Important immune cell types were identified through immunoinfiltration analysis in conjunction with single sample enrichment analysis (ssGSEA). Additionally, weighted co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was utilized to identify significantly associated genes. Finally, we employed LASSO regression, SVM-RFE, XGBoost, and random forest algorithms to further predict potential targets, followed by validation through molecular docking.
Results: Leeches may influence cellular immunity by modulating immune receptor activity, particularly through the activation of RGS10, CAPS2, and OPA1, thereby impacting the pathology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Discussion: However, it is important to note that our results lack experimental validation; therefore, further research is warranted to substantiate these findings.
Keywords: immune infiltrate; leech; machine learning; network pharmacology; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Hu and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bhatt D. L., Eikelboom J. W., Connolly S. J., Steg P. G., Anand S. S., Verma S., et al. (2020). Role of combination antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: insights from the COMPASS trial. Circulation 141 (23), 1841–1854. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046448 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camer D., Yu Y., Szabo A., Huang X. F. (2014). The molecular mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic properties of oleanolic acid, its isomer and derivatives for type 2 diabetes and associated complications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 58 (8), 1750–1759. Epub 2014/04/18. 10.1002/mnfr.201300861 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

