Expression of microRNAs in the detection and therapeutic roles of viral infections: Mechanisms and applications
- PMID: 40296890
- PMCID: PMC12034616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jve.2025.100586
Expression of microRNAs in the detection and therapeutic roles of viral infections: Mechanisms and applications
Abstract
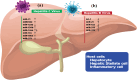
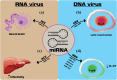
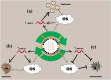
In recent years, microRNAs (miRNAs) are potential diagnostic and therapeutic agents for viral infections. Here, we aimed to investigate the expression of microRNAs in the identification and treatment of viral infections. MiRNAs are non-coding molecules that control gene expression and participate in numerous biological processes, including host immunity and pathogen duplication. MiRNAs have played a role in the pathogenesis of various viral infections, such as HIV and HCV. Their presence in the tissues and serum of infected patients has been demonstrated to help predict disease progression, identify disease subtypes, and evaluate treatment responses. Research has shown that miRNAs can detect viral infections by identifying specific miRNAs in serum. For example, miRNA expression profiling was recently used to distinguish between hepatitis C and hepatitis B viral infections precisely. Furthermore, miRNAs can be used to detect the presence of multiple viral infections simultaneously by assessing the expression levels of these miRNAs. Also, miRNAs can differentiate between different genetic variants of the same virus, which is useful for identifying emerging viral strains or drug-resistant ones. MiRNAs have been identified as being a factor in treating viral infections. For example, miRNA mimics have decreased gene expression and halted viral replication in HIV, HCV, and EBV. Moreover, microRNA antagonists have been utilized to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby modulating the immune response and the severity of infections.
Keywords: Barr virus; Epstein; Hepatitis B; Hepatitis C; Human immunodeficiency virus; MicroRNA.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple Viral microRNAs Regulate Interferon Release and Signaling Early during Infection with Epstein-Barr Virus.mBio. 2021 Mar 30;12(2):e03440-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03440-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33785626 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive overview on the crosstalk between microRNAs and viral pathogenesis and infection.Med Res Rev. 2025 Mar;45(2):349-425. doi: 10.1002/med.22073. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Med Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39185567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Viral and Host microRNAs in Immune Regulation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 3;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32194570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus Attenuate T-Cell-Mediated Immune Control In Vivo.mBio. 2019 Jan 15;10(1):e01941-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01941-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30647153 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of miRNA-122 in infectious diseases: Mechanisms and potential biomarkers.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Sep;249:154725. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154725. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37544130 Review.
References
-
- Abdel Halim A.S., Rudayni H.A., Chaudhary A.A., Ali M.A. MicroRNAs: small molecules with big impacts in liver injury. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2023;238(1):32–69. - PubMed
-
- Doghish A.S., Elballal M.S., Elazazy O., et al. The role of miRNAs in liver diseases: potential therapeutic and clinical applications. Pathology-Research and Practice. 2023 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

