Anticancer effects of SH003 and its active component Cucurbitacin D on oral cancer cell lines via modulation of EMT and cell viability
- PMID: 40296905
- PMCID: PMC12034017
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2025.059791
Anticancer effects of SH003 and its active component Cucurbitacin D on oral cancer cell lines via modulation of EMT and cell viability
Abstract
Background: Oral cancer remains a significant global health challenge, as it has high morbidity and mortality rates. Current treatments show limited efficacy and have severe side effects, prompting searches for new therapeutic agents. SH003, a traditional herbal formulation comprising Astragalus membranaceus, Angelica gigas, and Trichosanthes kirilowii, has demonstrated potential anticancer properties in previous studies. However, its specific efficacy against oral cancer and the role of its key components, particularly Cucurbitacin D, remain underexplored.
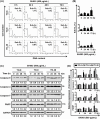
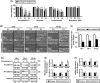
Methods: The cytotoxic effects of SH003 and its major components-i.e., Cucurbitacin D, Decursin, Formononetin, and Nodakenin-were evaluated using 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT), Trypan Blue exclusion, and Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) release assays. Cell migration was analyzed via wound healing assays, and apoptosis induction was assessed using cell cycle analysis and caspase activation assays. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker expression (E-cadherin and N-cadherin) was measured using Western blotting and Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR).
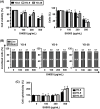
Results: SH003 significantly reduced cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, with YD-8 and YD-9 cells showing greater sensitivity than YD-38 cells. Of the individual compounds, Cucurbitacin D was identified as a key active agent, as it exhibited potent inhibition of cell migration and significant modulation of EMT markers, including the upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of N-cadherin. These effects were most pronounced in YD-9 cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, these findings suggest that Cucurbitacin D plays a crucial role mediating the anticancer activity of SH003, particularly via the reversal of EMT and the reduction of migratory and invasive potential of oral cancer cells. This study provides valuable insight into the mechanistic basis of SH003, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent against oral cancer. Further research, including in vivo studies and clinical trials, is needed to elucidate its precise mechanisms and potential applications against other cancer types.
Keywords: Cucurbitacin D; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT); Migration; Oral cancer; SH003.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
