Current innovations in head and neck cancer: From diagnostics to therapeutics
- PMID: 40296914
- PMCID: PMC12034008
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2025.060601
Current innovations in head and neck cancer: From diagnostics to therapeutics
Abstract
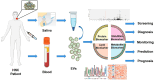
Background: Head and neck cancers (HNC) account for a significant global health burden, with increasing incidence rates and complex treatment requirements. Traditional diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, while effective, often result in substantial morbidity and limitations in personalized care. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the latest innovations in diagnostics and therapeutic strategies for HNC from 2015 to 2024.
Methods: A review of literature focused on pe-reviewed journals, clinical trial databases, and oncology conference proceedings. Key areas include molecular diagnostics, imaging technologies, minimally invasive surgeries, and innovative therapeutic strategies.
Results: Technologies like liquid biopsy next-generation sequencing (NGS) have greatly improved diagnostic accuracy and personalization in HNC care. These advancements have improved survival rates and enhanced patients' quality of life. Personalized therapeutic approaches, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, precision radiation therapy, and surgery, have led to enhanced treatment efficacy while reducing side effects. The integration of AI and machine learning into diagnostics and treatment planning shows promise in optimizing clinical decision-making and predicting treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: The current innovations in diagnostics and therapeutics are reshaping the management of head and neck cancer, offering more tailored and effective approaches to care. Overall, the continuous integration of these innovations in clinical practice is reshaping HNC treatment and improving patient outcomes and survival rates. Future research should focus on further refining these technologies, addressing challenges related to accessibility, and exploring their long-term clinical benefits in diverse patient populations.
Keywords: Diagnostics; Head and neck cancer (HNC); Innovations; Therapeutics.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Head and Neck Cancer: Innovations, Applications, and Future Directions.Curr Oncol. 2024 Sep 6;31(9):5255-5290. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31090389. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39330017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-Driven Biomarker Discovery and Personalized Allergy Treatment: Utilizing Machine Learning and NGS.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025 Jun 3;25(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s11882-025-01207-8. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025. PMID: 40459653 Review.
-
Advancing head and neck cancer management: Unveiling the diagnostic and therapeutic potentials of molecular profiling.Head Neck. 2024 Oct;46(10):E84-E90. doi: 10.1002/hed.27882. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Head Neck. 2024. PMID: 39032143
-
Advancing Veterinary Oncology: Next-Generation Diagnostics for Early Cancer Detection and Clinical Implementation.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;15(3):389. doi: 10.3390/ani15030389. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
