Assessment of Long-Term Outcomes of Lower Limb Fractures Managed by Non-orthopaedic Specialist Surgeons in Rural Rwanda: A Pilot Feasibility Study
- PMID: 40296977
- PMCID: PMC12034499
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81323
Assessment of Long-Term Outcomes of Lower Limb Fractures Managed by Non-orthopaedic Specialist Surgeons in Rural Rwanda: A Pilot Feasibility Study
Abstract
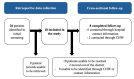
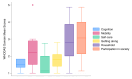
Introduction Sub-Saharan Africa is disproportionately affected by injuries, and short-term morbidity and mortality are high in this context. Lower limb fractures (LLFs) are a common type of injury that can lead to severe disability with extensive negative social and economic consequences. However, little is known about the long-term outcomes of LLFs in sub-Saharan Africa. In this pilot study, we describe the feasibility of assessing epidemiological patterns of LLFs, the state of care, and long-term outcomes in rural Rwanda. Methods This study was conducted from July to December 2021. It consists of retrospective data collection from hospital charts and a cross-sectional, phone-based follow-up. Functional outcomes were assessed using the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS; World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland) 2.0, and health-related quality of life (QoL) was assessed using a 36-Item Short Form Health Survey questionnaire (SF-36). Results Eighteen patients were included in the study, of which the majority were males (n=11, 61%), young adults (mean age 29, standard deviation (SD) 25), and without any previous comorbidities (n=16, 89%). Most patients had a single fracture, although nearly one-third presented with multi-trauma (n=5, 28%). The most common injury cause was falls (n=10, 56%). Fractures were most common in the femur/hip (n=10, 56%), and most fractures were closed (n=14, 78%) and non-comminuted (n=9, 50%). Disability was described as high, with a total mean WHODAS summary score of 80 (SD 29), whereas health-related QoL varied across the SF-36 domains, with "general health" being the lowest rated domain with a mean score of 30 (SD 25). Conclusion This study highlights the challenges of long-term follow-up after LLFs in a rural, low-resource setting but demonstrates that such a study is feasible if planned with contextual considerations. Self-perceived disability is high, and health-related QoL is low at long-term follow-up, which should be viewed in light of the fact that it primarily affects a young, previously healthy population.
Keywords: east africa; functional and clinical outcome; functional disability; health-related quality of life; long-term outcome; low- and middle-income country; lower extremity trauma.
Copyright © 2025, Velin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Rwanda National Ethics Committee issued approval No.141RNEC/2023. The study was approved by the Rwanda National Ethics Committee on May 5, 2023. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: Barnabas Alayande and Alex Zhuang are supported by the Fogarty International Center and National Institute of Mental Health, of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number D43 TW010543. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. . Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Trauma mortality patterns in three nations at different economic levels: implications for global trauma system development. Mock CN, Jurkovich GJ, nii-Amon-Kotei D, et al. https://journals.lww.com/jtrauma/abstract/1998/05000/trauma_mortality_pa.... J Trauma. 1998;44:804–812. - PubMed
-
- Current status of musculoskeletal trauma care systems worldwide. Miclau T, Hoogervorst P, Shearer DW, et al. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32 Suppl 7:0–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
