Research landscape and trends of internet addiction disorder: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of publications in the past 20 years
- PMID: 40297375
- PMCID: PMC12034966
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076251336940
Research landscape and trends of internet addiction disorder: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of publications in the past 20 years
Abstract
Background: Internet addiction disorder (IAD) has emerged as a significant public health concern in the digital age, with implications for mental health and social wellbeing. Despite growing recognition, IAD remains a relatively nascent field within academic research.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis to explore the global research landscape and trends of IAD. Our methodology involved analyzing author analysis, journal analysis, keywords, and citations in publications related to IAD from 2004 to 2024.
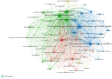
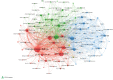
Results: We identified "internet addiction," "internet gaming disorder," and "adolescent" as the most frequently occurring keywords, highlighting significant research areas within IAD. The analysis revealed that terms like "social media addiction," "problematic smartphone use," and "COVID-19" have gained prominence in recent years, reflecting the evolving nature of digital technology's impact on mental health. Clustering analysis illustrated the interdisciplinary nature of IAD research, integrating insights from psychology, sociology, network science, and psychiatry. Citation analysis identified highly influential papers, such as Kuss and Griffiths' review on social networking addiction and Brand et al.'s I-PACE model for internet-use disorders.
Conclusions: Our findings highlighted the importance of continuing interdisciplinary research to address the multifaceted challenges of IAD. Future research should focus on the intersections of digital behaviors with mental health, personality traits, and social dynamics to develop comprehensive strategies for prevention and intervention.
Keywords: Internet addiction disorder; bibliometric analysis; internet gaming disorder; mental health; problematic smartphone use; social media addiction.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Exploring the relationship between social media dependence and internet addiction among college students from a bibliometric perspective.Front Psychol. 2025 Mar 12;16:1463671. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1463671. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40144033 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the Web of Influence: A Bibliometric Analysis of Social Media Addiction.Cureus. 2024 Jun 13;16(6):e62283. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62283. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39006596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Research into Internet Gaming Disorders in Korea.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 21;20(5):3786. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20053786. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36900797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Internet Addiction and Mental Disorders in Medical Students: A Systematic Review.Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023 Jun 6;25(3):22r03384. doi: 10.4088/PCC.22r03384. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023. PMID: 37310317
-
Electroencephalography-detected neurophysiology of internet addiction disorder and internet gaming disorder in adolescents - A review.Med J Malaysia. 2021 May;76(3):401-413. Med J Malaysia. 2021. PMID: 34031341 Review.
References
-
- Weinstein A, Lejoyeux M. Internet addiction or excessive internet use. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 2010; 36: 277–283. - PubMed
-
- Petry NM, Rehbein F, Ko C-H, et al. Internet gaming disorder in the DSM-5. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2015; 17: 72. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Chen J, Wang P, et al. Identifying Internet addiction profiles among adolescents using latent profile analysis: relations to aggression, depression, and anxiety. J Affect Disord 2024; 359: 78–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

