Peptide-specific natural killer cell receptors
- PMID: 40297637
- PMCID: PMC12036969
- DOI: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqaf003
Peptide-specific natural killer cell receptors
Abstract
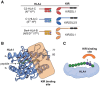
Class I and II human leukocyte antigens (HLA-I and HLA-II) present peptide antigens for immunosurveillance by T cells. HLA molecules also form ligands for a plethora of innate, germline-encoded receptors. Many of these receptors engage HLA molecules in a peptide sequence independent manner, with binding sites outside the peptide binding groove. However, some receptors, typically expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, engage the HLA presented peptide directly. Remarkably, some of these receptors display exquisite specificity for peptide sequences, with the capacity to detect sequences conserved in pathogens. Here, we review evidence for peptide-specific NK cell receptors (PSNKRs) and discuss their potential roles in immunity.
Keywords: HLA-I; KIR; MHC-I; NK cell; NKG2A/C.
Published by Oxford University Press 2025.
Figures

References
-
- Janeway CA Jr., Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Raulet DH. Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat Rev Immunol 2003;3:781–90. - PubMed
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M et al. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 2008;9:503–10. - PubMed
-
- Male V, Moffett A. Natural killer cells in the human uterine mucosa. Annu Rev Immunol 2023;41:127–51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
