Multifunctional piezoelectric hydrogels under ultrasound stimulation boost chondrogenesis by recruiting autologous stem cells and activating the Ca2+/CaM/CaN signaling pathway
- PMID: 40297641
- PMCID: PMC12036080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.04.009
Multifunctional piezoelectric hydrogels under ultrasound stimulation boost chondrogenesis by recruiting autologous stem cells and activating the Ca2+/CaM/CaN signaling pathway
Abstract
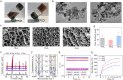
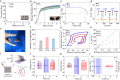
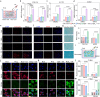
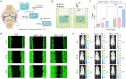
Articular cartilage, owing to the lack of undifferentiated stem cells after injury, faces significant challenges in reconstruction and repair, making it a major clinical challenge. Therefore, there is an urgent need to design a multifunctional hydrogels capable of recruiting autologous stem cells to achieve in situ cartilage regeneration. Here, our study investigated the potential of a piezoelectric hydrogel (Hyd6) for enhancing cartilage regeneration through ultrasound (US) stimulation. Hyd6 has multiple properties including injectability, self-healing capabilities, and piezoelectric characteristics. These properties synergistically promote stem cell chondrogenesis. The fabrication and characterization of Hyd6 revealed its excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, and electromechanical conversion capabilities. In vitro and in vivo experiments revealed that Hyd6, when combined with US stimulation, significantly promotes the recruitment of autologous stem cells and enhances chondrogenesis by generating electrical signals that promote the influx of Ca2+, activating downstream CaM/CaN signaling pathways and accelerating cartilage formation. An in vivo study in a rabbit model of chondral defects revealed that Hyd6 combined with US treatment significantly improved cartilage regeneration, as evidenced by better integration of the regenerated tissue with the surrounding cartilage, greater collagen type II expression, and improved mechanical properties. The results highlight the potential of Hyd6 as a novel therapeutic approach for treating cartilage injuries, offering a self-powered, noninvasive, and effective strategy for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Bioadhesiveness; Calcium ion; Chondrogenesis; Piezoelectric hydrogel; Ultrasound stimulation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
In the manuscript entitled “Multifunctional piezoelectric hydrogels under ultrasound stimulation boosts chondrogenesis by recruiting autologous stem cells and activating Ca2+/CaM/CaN signal pathway", the authors declare that there are no competing financial and/or non-financial interests associated with the work described. All authors involved in this study have adhered to the relevant ethical guidelines, ensuring the independence and objectivity of the research. Specifically, this research has not been influenced by any commercial or personal interests that could affect the interpretation or reporting of the study results. The authors have no stocks or ownership interests related to this research, nor have they received any remuneration, funding, or any form of compensation for conducting, designing, or reporting the research. Furthermore, the authors have no affiliations with any organizations or entities that may benefit or be adversely affected by the results of this study. We further declare that the results reported in this study are accurate and have not been subjected to any form of manipulation or selective reporting to conform to any specific outcomes or conclusions. The authors assume full responsibility for the integrity and impartiality of the research. All individuals listed as authors have reviewed this statement and confirm its accuracy and completeness.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

