This is a preprint.
IL-9 and Blimp-1 protects the transcriptional identity of group 2 innate lymphocytes in allergic asthma
- PMID: 40297693
- PMCID: PMC12036457
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6365283/v1
IL-9 and Blimp-1 protects the transcriptional identity of group 2 innate lymphocytes in allergic asthma
Abstract
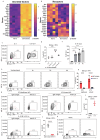
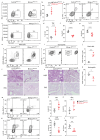
Allergic asthma is driven by type 2 immune cells including type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). ILC2s respond to the tissue alarmins IL-33 and IL-25, however these signals do not uniquely promote type 2 inflammation, and the factors that maintain ILC2s ability to produce type 2 cytokines are not known. Here, we show that allergen-driven tissue alarmins IL-33 and IL-25 rapidly induce IL-9, which directly upregulates the transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 through an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Blimp-1 promotes type 2 responses by directly repressing type 1 inflammation including the cytokines IFNγ and TNF. Deletion of Blimp-1 in ILC2s increases type 1 cytokines and concomitantly reduces type 2 cytokines, ameliorating mucus production and airway inflammation in response to allergens. Thus, Blimp-1 maintains the type 2 transcriptional identity of ILC2s in response to inflammation, driving type 2 immunity and allergic asthma.
Figures









References
-
- Lambrecht B. N. & Hammad H. The immunology of asthma. Nat Immunol 16, 45–56 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

