Social media and internet use among orthopedic patients in Germany-a multicenter survey
- PMID: 40297730
- PMCID: PMC12035442
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1486296
Social media and internet use among orthopedic patients in Germany-a multicenter survey
Abstract
Background: Social media (SM) is increasingly used in the healthcare system and offers various benefits for patients such as accessible health information and communication with other patients and healthcare professionals. However, SM also poses risks, including the dissemination of medical misinformation and privacy concerns. This in turn can influence patients' health-related decision-making and the patient-physician relationship. There is limited data regarding which SM orthopedic patients use and what benefits and risks of SM they perceive.
Methods: An online survey was conducted from April to December 2023 among orthopedic and trauma patients in five German orthopedic clinics. The questionnaire with 32 variables was designed to assess internet and SM usage patterns, platform preferences, and perceived benefits and risks. Statistical analysis was performed, including subgroup analyses.
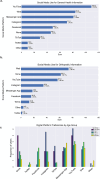
Results: A total of 267 patients participated, with 82.0% reporting regular SM use. In total 45.9% of the patients used SM for general health questions and 51.3% for orthopedic-related questions. The most used information platforms were conventional websites, YouTube, Instagram, and messenger apps. A total of 45.9% used SM infrequently for general health questions, and 51.3% for orthopedic-related queries. Only 13.7% of patients agreed that SM helped in medical decision-making, and 31.1% felt confident in assessing the credibility of SM content. Additionally, 58.6% of patients were unsure about allowing physicians to present their cases on SM, and 62.3% were uncertain about posting their medical images.
Conclusion: Among German orthopedic patients, the use of SM for health-related and gain of orthopedic information was low in the given study. While SM may offer valuable health information, their role in medical decision-making remains limited due to concerns over content credibility and privacy. Video-based content seems to achieve the best reach. Future research should explore these aspects longitudinally and across diverse populations to better understand and address the challenges and benefits of SM in healthcare.
Keywords: communication; digitalization; orthopedics; patients; social media.
© 2025 Youssef, Vu-Han, Trauth, Osterhoff, Back and Gehlen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akram W, Kumar R. A study on positive and negative effects of social Media on society. Int J Comput Sci Eng. (2017) 5:351–4. 10.26438/ijcse/v5i10.351354 - DOI
-
- Siddiqui S, Singh T. Social media its impact with positive and negative aspects. Int J Comput Appl Technol Res. (2016) 5:71–5. 10.7753/IJCATR0502.1006 - DOI
-
- Duffett RG. Influence of social media marketing communications on young consumers’ attitudes. Young Consum. (2017) 18:19–39. 10.1108/YC-07-2016-00622 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

