Anti-PF4 mediated thrombocytopenia and thrombosis associated with acute cytomegalovirus infection displays both HIT-like and VITT-like characteristics
- PMID: 40298004
- PMCID: PMC12166337
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.20092
Anti-PF4 mediated thrombocytopenia and thrombosis associated with acute cytomegalovirus infection displays both HIT-like and VITT-like characteristics
Abstract
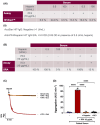
Vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT) is one of several anti-platelet factor 4 (anti-PF4)-associated immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (PITT) syndromes. As well as following adenoviral vector vaccines, VITT has recently been described following acute adenovirus infection. We describe a patient with PITT following acute cytomegalovirus infection. The antibody clonotype and PF4 epitopes were distinct from those identified in VITT, and they were detectable as a paraprotein. PITT should be considered in all patients with thrombocytopenia and thrombosis, even without preceding vaccination or heparin, but who otherwise meet the VITT criteria defined by the British Society of Haematology Expert Panel.
Keywords: FCY receptor; cytomegalovirus; heparin‐induced TP; monoclonal antibodies; platelet activation; platelet factor 4; thrombocytopenia; thrombosis.
© 2025 The Author(s). British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
PLRN has received research support from Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Rigel and Sanofi, has provided consultancy services for Sobi and has received speaker fees from Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Sobi & Takeda. RJB has received research support from Astra Zeneca. TEW has received research support from Werfen and has provided consulting services for Instrumentation Laboratory Company, Octapharma, Paradigm Pharmaceuticals, Veralox Therapeutics and Wefen. WAL has received speaker fees from Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Baichi Sankyo and Pfizer.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

