Tirzepatide vs semaglutide and liraglutide for weight loss in patients with overweight or obesity without diabetes: A short-term cost-effectiveness analysis in the United States
- PMID: 40298310
- PMCID: PMC12039506
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2025.31.5.441
Tirzepatide vs semaglutide and liraglutide for weight loss in patients with overweight or obesity without diabetes: A short-term cost-effectiveness analysis in the United States
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and their analogues have emerged as effective pharmacotherapies for obesity.
Objective: To assess the short-term cost-effectiveness of subcutaneous tirzepatide, semaglutide, liraglutide, and oral semaglutide for managing obesity or overweight in patients without diabetes.
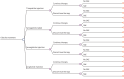
Methods: A decision tree model was developed using a 68-week time window with consideration of serious adverse events and treatment discontinuation from a US payer's perspective. The study population were adults with obesity or overweight with at least 1 weight-related comorbidity but without diabetes. Clinical data were obtained from clinical trials. Model utilities, disutilities, and the costs of serious adverse events were sourced from published literature. Medication costs were assigned from Red Book. All costs were calculated in 2024 US dollars. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated based on the cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained. A willingness-to-pay threshold of $150,000 per QALY was used. One-way sensitivity analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis were performed to assess the effect of parameter uncertainty on the results.
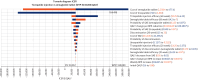
Results: In the base-case analysis, both subcutaneous tirzepatide and oral semaglutide were cost-effective vs subcutaneous liraglutide and subcutaneous semaglutide. Compared with oral semaglutide, subcutaneous tirzepatide was cost-effective, with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $34,212 per QALY gained. Sensitivity analyses indicated the results were highly sensitive to medication costs and the effectiveness of medications. The probabilistic sensitivity analysis suggested that subcutaneous tirzepatide was most likely to remain cost-effective, with a 98% probability at a willingness to pay of $150,000 per QALY compared with other medications.
Conclusions: Subcutaneous tirzepatide and oral semaglutide were cost-effective therapies compared with subcutaneous liraglutide and subcutaneous semaglutide for the short-term management of obesity in adults without diabetes. At or under a willingness-to-pay threshold of $150,000 per QALY, subcutaneous tirzepatide was most cost-effective, surpassing oral semaglutide. These findings provide valuable insights for health care decision-makers in selecting antiobesity medications.
Figures

References
-
- Phelps NH, Singleton RK, Zhou B, et al. ; NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet . 2024;403(10431):1027-50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02750-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Adult obesity facts. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. March 19, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult-obesity-facts/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

