Cost-effectiveness analysis of targeted-release formulation of budesonide (Tarpeyo) in conjunction with optimized renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) therapy relative to optimized RASi therapy alone for adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy in the United States
- PMID: 40298312
- PMCID: PMC12041922
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2025.31.5.499
Cost-effectiveness analysis of targeted-release formulation of budesonide (Tarpeyo) in conjunction with optimized renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) therapy relative to optimized RASi therapy alone for adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy in the United States
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) is a rare autoimmune disease that often leads to end-stage renal disease. The goal of treatment is to reduce disease progression so that patients are less likely to develop kidney failure in their natural lifetime. Recent clinical trial results show that Tarpeyo, a targeted-release formulation of budesonide designed to deliver the drug directly to gut-associated lymphoid tissue, reduces estimated glomerular filtration rate loss, potentially modifying the disease and thus prolonging the time to kidney failure.
Objective: To assess the cost-effectiveness of Tarpeyo in conjunction with optimized renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) therapy relative to optimized RASi therapy alone in US adult patients with primary IgAN.
Methods: A cost-utility approach is taken based on the full dataset from the phase 3 NefIgArd clinical trial. A semi-Markov model was developed with a lifetime horizon, encompassing both the US commercial payer and societal perspectives. The model architecture incorporated 9 health states, reflecting varying degrees of disease severity and mortality. Transition probabilities between health states were determined by a robust regression analysis of individual patient-level data obtained from the NefIgArd clinical trial and supplemented with data from literature. In the base-case analysis, treatment effect was assumed to be continuously maintained over the model time horizon (lifetime) and treatment was reapplied every 2 years. Treatment cost, adverse event management, dialysis, transplantation, mortality costs, and indirect costs were considered.
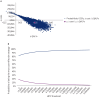
Results: Tarpeyo + optimized RASi was found to be dominant compared with optimized RASi alone from the perspective of a US third-party commercial payer, ie, cost saving ($105 729) with concurrent quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gains of 1.12. The base-case results show that Tarpeyo is dominant when retreatment occurs every 2 years, with the treatment benefit assumed to be maintained over the same period throughout the model. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of the base-case results, showing that Tarpeyo plus optimized RASi is cost saving if benefits are sustained for at least 3 years. The treatment demonstrated high probabilities of cost-effectiveness at willingness-to-pay thresholds of less than $100K and less than $150K per QALY.
Conclusions: Clinical trials suggest that adding Tarpeyo to optimized RASi can help preserve kidney function by reducing estimated glomerular filtration rate loss in patients with IgAN. This addition was estimated to produce a greater QALY gain and reduced overall net costs from the payer and societal perspective in the United States.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Yaghoubi, Mr Jian, and Mr Casciano are employees of Certara, Inc. Mr Ngai and Dr Patel (at the time of manuscript submission) are employees of Calliditas NA Enterprises, Inc. This study was funded by Calliditas NA Enterprises, Inc. Calliditas NA Enterprises, Inc., provided input into the initial study concept and design but had no influence over the study execution and the decision to publish.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Nefecon versus Best Supportive Care for People with Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN) in the United States.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2023 Mar 29;15:213-226. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S389456. eCollection 2023. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2023. PMID: 37020570 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of inhibitors of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS) and combination therapy of steroids plus RAS inhibitors for patients with advanced immunoglobulin A nephropathy and impaired renal function.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012 Apr;16(2):231-7. doi: 10.1007/s10157-011-0545-7. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22038185
-
Insights on Nefecon®, a Targeted-Release Formulation of Budesonide and Its Selective Immunomodulatory Effects in Patients with IgA Nephropathy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 31;18:3415-3428. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S383138. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39100224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of budesonide/formoterol SMART therapy versus salmeterol/fluticasone plus as-needed SABA among patients ≥12 years with moderate asthma from the Chinese societal perspective.J Med Econ. 2024 Jan-Dec;27(1):1018-1026. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2024.2385191. Epub 2024 Aug 17. J Med Econ. 2024. PMID: 39067014
-
Association between early worsening of kidney function and poor outcomes in patients treated with renin angiotensin system inhibitors: A meta-analysis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2021 Oct;26(10):772-781. doi: 10.1111/nep.13915. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Nephrology (Carlton). 2021. PMID: 34165226 Review.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System . USRDS Annual Data Report 2020. Chapter 6: healthcare expenditures for persons with CKD. ESRD in the United States. 2020. Accessed August 20, 2024. https://adr.usrds.org/2020/chronic-kidney-disease/6-healthcare-expenditu...
-
- United States Renal Data System . USRDS Annual Data Report 2022. Chapter 9: healthcare expenditures for persons with ESRD. ESRD in the United States. 2022. Accessed August 20, 2024. https://usrds-adr.niddk.nih.gov/2024
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources