Donor-Related Risk Factors for Normothermic Machine Perfusion in Liver Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40298438
- PMCID: PMC12039471
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70116
Donor-Related Risk Factors for Normothermic Machine Perfusion in Liver Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
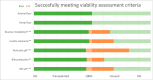
Background and aims: During normothermic machine perfusion (NMP), a variety of criteria are used to gauge the suitability of an organ for transplantation. However, the relations between donor factors and these criteria are poorly understood. The aim of this meta-analysis was to investigate the association between donor-related risk factors and the decision to transplant a liver subjected to NMP.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed for articles published up to March 2025 in four databases, reporting livers subjected to NMP for viability assessment prior to transplantation. Effect size (ES) was calculated using Cohen's D and log odds ratio.
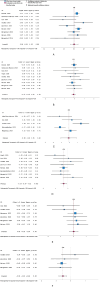
Results: Out of 806 unique articles, 18 were included in this meta-analysis, encompassing 690 liver grafts that underwent NMP. Following viability assessment during NMP, utilisation rate was 82% from donors after brain death and 68% from donors after circulatory death (ES: 0.08, p = 0.88). Transplanted livers had shorter cold ischemia time (ES: -0.34, p = 0.003) and lower liver weight (ES: -0.53, p < 0.001). Donor age, BMI and donor warm ischemia time did not differentiate between transplanted and unused groups. Differences were observed in viability assessment for lactate clearance (ES: 2.0, p = 0.005), glucose metabolism (ES: 2.2, p < 0.001), bile production (ES: 1.0, p = 0.003) and pH (ES: 1.9, p < 0.001). Excellent outcomes, including 10% non-anastomotic strictures, 89% graft survival and 93% patient survival, were achieved in a large cohort of high-risk livers.
Conclusion: Cold ischemia time and liver weight were identified as donor-related risk factors, whereas donor type, age and donor warm ischemia time appear not to impact the decision to transplant during NMP.
Keywords: diagnosis; metabolism; methods; mortality; therapy; transplantation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eurotransplant International Foundation , “Statistics Report Library,” EIF.
-
- Kalisvaart M., Croome K. P., Hernandez‐Alejandro R., et al., “Donor Warm Ischemia Time in DCD Liver Transplantation‐Working Group Report From the ILTS DCD, Liver Preservation, and Machine Perfusion Consensus Conference,” Transplantation 105, no. 6 (2021): 1156–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

