Nuclear-Localized BCKDK Facilitates Homologous Recombination Repair to Support Breast Cancer Progression and Therapy Resistance
- PMID: 40298908
- PMCID: PMC12165075
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202416590
Nuclear-Localized BCKDK Facilitates Homologous Recombination Repair to Support Breast Cancer Progression and Therapy Resistance
Abstract
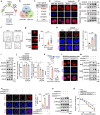
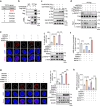
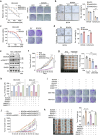
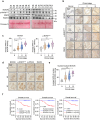
Homologous recombination repair (HRR) is crucial for maintaining genomic stability by repairing DNA damage. Despite its importance, HRR's role in cancer progression is not fully elucidated. Here, this work shows that nuclear-localized branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BCKDK) acts as a modulator of HRR, promoting cell resistance against DNA damage-inducing therapy in breast cancer. Mechanistically, this work demonstrates that BCKDK is localized in the nucleus and phosphorylates RNF8 at Ser157, preventing the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of RAD51, thereby facilitating HRR-mediated DNA repair under replication stress. Notably, aberrant expression of the BCKDK/p-RNF8/RAD51 axis correlates with breast cancer progression and poor patient survival. Furthermore, this work identifies a small molecule inhibitor of BCKDK, GSK180736A, that disrupts its HRR function and exhibits strong tumor suppression when combined with DNA damage-inducing drugs. Collectively, this study reveals a new role of BCKDK in regulating HRR, independent of its metabolic function, presenting it as a potential therapeutic target and predictive biomarker in breast cancer.
Keywords: BCKDK; DNA repair inhibitor; breast cancer; combinational therapy; homologous recombination repair.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chapman J. R., Taylor M. R. G., Boulton S. J., Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 497. - PubMed
-
- Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 739. - PubMed
-
- Halazonetis T. D., Gorgoulis V. G., Bartek J., Science 2008, 319, 1352. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J., Rezaei N., Liontos M., Karakaidos P., Kletsas D., Issaeva N., Vassiliou L. V. F., Kolettas E., Niforou K., Zoumpourlis V. C., Takaoka M., Nakagawa H., Tort F., Fugger K., Johansson F., Sehested M., Andersen C. L., Dyrskjot L., Orntoft T., Lukas J., Kittas C., Helleday T., Halazonetis T. D., Bartek J., Gorgoulis V. G., Nature 2006, 444, 633. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1304504/National Key R&D Program of China
- 82430097/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32450194/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82192893/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82130087/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341013/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82372820/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- XDB0940101/Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- XDB0940202/Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- WK9100000081/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- QYPY20230029/Comprehensive National Science Center, Research Funds of Center for Advanced Interdisciplinary Science and Biomedicine of IHM
- DJK-LX-2022001/the Global Select Project of the Institute of Health and Medicine, Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
