Elevated Serum SERPINE2 Levels are Linked to Impaired Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 40299282
- PMCID: PMC12085428
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-025-01742-7
Elevated Serum SERPINE2 Levels are Linked to Impaired Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the primary complication associated with diabetes mellitus and is increasingly acknowledged as the leading cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide, placing a significant economic burden on society. This study determined how blood serpin peptidase inhibitor clade E member 2 (SERPINE2) levels affect DN in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
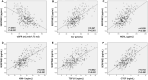
Methods: We recruited 292 individuals diagnosed with T2DM and 120 healthy controls for this study. We employed comprehensive and systematic data collection methodologies to gather relevant biomarkers and information on biochemical parameters. We measured serum levels of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGFβ1), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and SERPINE2 by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in control subjects and patients with T2DM. We calculated generalized odds ratios (OR) to estimate the risk of developing DN.
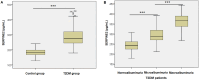
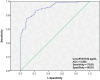
Results: Patients with diabetes had significantly higher levels of SERPINE2 (285.64 ± 56.58 pg/mL) than healthy controls (184.84 ± 23.54 pg/mL). Additionally, the multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that patients with diabetes with DN possessed higher levels of serum SERPINE2 (OR 1.033, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.013-1.053; P = 0.001), along with an increased body mass index (BMI), duration of diabetes, serum creatinine (Scr), NGAL, KIM-1, TGFβ1, and CTGF. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis indicated that patients with T2DM and serum SERPINE2 levels exceeding 278.94 pg/mL had a significantly higher risk of developing DN.
Conclusion: The results showed that patients with diabetes with DN have higher levels of serum SERPINE2. A more extensive population-based prospective study is needed to validate our findings.
Keywords: Biomarker; Diabetic nephropathy; Estimated glomerular filtration rate; SERPINE2; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: The authors Shudan Cao, Qing Tan, and Lijuan Yang have nothing to disclose. Ethical Approval: The Ethics Committee of Sijing Hospital granted approval for this study (SJYY202401-YNKT-CSD). The authors adhered to all standard protocols in line with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects participating in the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, kidney injury molecule-1, and periostin: Novel urinary biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy.World J Nephrol. 2024 Dec 25;13(4):98880. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v13.i4.98880. World J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39723350 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Podoplanin Levels as a Potential Biomarker for Diabetic Nephropathy Progression: A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Dec 6;17:4701-4710. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S500608. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39660339 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Lipocalin-2 Levels Are Increased and Independently Associated With Early-Stage Renal Damage and Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque in Patients With T2DM.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 25;13:855616. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.855616. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35547005 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Predicting Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Appl Lab Med. 2019 Jul;4(1):78-94. doi: 10.1373/jalm.2018.028530. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Appl Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31639710
-
Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2749-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Demir Y, Ceylan H, Türkeş C, Beydemir Ş. Molecular docking and inhibition studies of vulpinic, carnosic and usnic acids on polyol pathway enzymes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(22):12008–21. - PubMed
-
- Sever B, Altıntop MD, Demir Y, et al. Design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico investigation of aldose reductase inhibitory effects of new thiazole-based compounds. Bioorg Chem. 2020;102:104110. - PubMed
-
- Bellary S, Kyrou I, Brown JE, Bailey CJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults: clinical considerations and management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(9):534–48. - PubMed
-
- Hu Q, Chen Y, Deng X, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: focusing on pathological signals, clinical treatment, and dietary regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;159:114252. - PubMed
-
- Sharma D, Bhattacharya P, Kalia K, Tiwari V. Diabetic nephropathy: new insights into established therapeutic paradigms and novel molecular targets. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:91–108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

