The Elevation and Impact of Peripheral Bile Acids in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 40299495
- PMCID: PMC12024544
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13040874
The Elevation and Impact of Peripheral Bile Acids in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
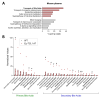
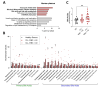
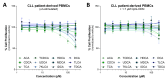
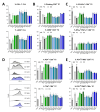
Background: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most prevalent adult leukemia in the Western world. Targeted therapies have made CLL manageable for many patients, but the ongoing threat of disease relapse or transformation beckons a deeper understanding of CLL pathogenesis, and thus, its durable eradication. This study identifies bile acids (BAs) as elevated in the peripheral blood of CLL patients and a murine model of CLL, in comparison to healthy controls. Elevated BA concentrations have been associated with intestinal malignancies and immunomodulation; however, their role in CLL is relatively unknown. Methods: Metabolomic analysis was performed on murine and human plasma. Flow cytometry analysis of CLL patient B-cells and healthy donor T-cells were utilized to evaluate the immunomodulatory impact of differentially abundant BAs. Results: Herein, BAs were found to be differentially abundant in CLL. Elevated BAs demonstrated minimal impact on CLL cell proliferation or CLL-associated T-cell function. Conclusions: Future studies are needed to determine the mechanistic influence of BAs on CLL pathogenesis.
Keywords: TCL1 mouse model; bile acids; chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L.S, A.R., S.A.S., R.M.R., E.M.D., and E.M. declare no conflict of interest. C.R.D. consults for Abbvie, Genmab, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Beigene, and Curis Inc. C.R.D. has received research funding from Fate Therapeutics, BeiGene, Curis Inc., and Bristol-Myers-Squibb. C.R.D and D.E.-G. and have received research funding from AbbVie.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

