Druggability Studies of Benzene Sulfonamide Substituted Diarylamide (E3) as a Novel Diuretic
- PMID: 40299675
- PMCID: PMC12024912
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13040992
Druggability Studies of Benzene Sulfonamide Substituted Diarylamide (E3) as a Novel Diuretic
Abstract
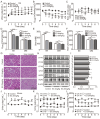
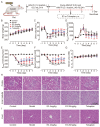
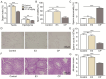
Background/Objectives: Urea transporters (UTs) play an important role in the urine-concentrating mechanism and have been regarded as a novel drug target for developing salt-sparing diuretics. Our previous studies found that diarylamides 1H and 25a are specific UT inhibitors and have oral diuretic activity. However, these compounds necessitate further optimization and comprehensive druggability studies. Methods: The optimal compound was identified through structural optimization. Experiments were conducted to investigate its UT inhibitory activity and evaluate its diuretic effect. Furthermore, disease models were utilized to assess the compound's efficacy in treating hyponatremia. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed to examine its metabolic stability, and toxicity tests were conducted to evaluate its safety. Results: Based on the chemical structure of compound 25a, we synthesized a novel diarylamide compound, E3, by introducing a benzenesulfonamide group into its side chain. E3 exhibited dose-dependent inhibition of UT at the nanomolar level and demonstrated oral diuretic activity without causing electrolyte excretion disorders in both mice and rats. Experiments on UT-B-/- and UT-A1-/- mice indicated that E3 enhances the diuretic effect primarily by inhibiting UT-A1 more effectively than UT-B. Furthermore, E3 displayed good metabolic stability and favorable pharmacokinetic characteristics. E3 significantly ameliorated hyponatremia through diuresis in a rat model. Importantly, E3 did not induce acute oral toxicity, subacute oral toxicity, genotoxicity, or cardiotoxicity. Conclusions: Our study confirms that E3 exerts a diuretic effect by specifically inhibiting UTs and has good druggability, which offers potential for E3 to be developed into a new diuretic for the treatment of hyponatremia.
Keywords: diuretic; hyponatremia; pharmacokinetic; safety evaluation; structure optimization; urea transporter inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Jing Li and Yinglin Zuo were employed by the company Sunshine Lake Pharma Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Inker L.A., Grams M.E., Levey A.S., Coresh J., Cirillo M., Collins J.F., Gansevoort R.T., Gutierrez O.M., Hamano T., Heine G.H., et al. Relationship of Estimated GFR and Albuminuria to Concurrent Laboratory Abnormalities: An Individual Participant Data Meta-analysis in a Global Consortium. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019;73:206–217. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.08.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatur S., Vaduganathan M., Claggett B., Vardeny O., Desai A.S., Jhund P.S., de Boer R.A., Lam C.S.P., Kosiborod M.N., Shah S.J., et al. Dapagliflozin and diuretic utilization in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction: The DELIVER trial. Eur. Heart J. 2023;44:2930–2943. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad283. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

