Characterization of human cytomegalovirus infection dynamics in human microglia
- PMID: 40299764
- PMCID: PMC12041478
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.002096
Characterization of human cytomegalovirus infection dynamics in human microglia
Abstract
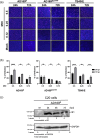
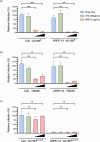
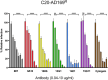
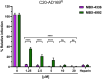
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a β-herpesvirus that establishes asymptomatic infections in immunocompetent individuals but can cause severe or even life-threatening symptoms in immunocompromised patients. HCMV can replicate in a wide variety of cells through the engagement of diverse cell factors with the viral envelope protein gH/gL/gO (trimer) or gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL131a (pentamer), allowing for systemic spread within the human host. This study explores HCMV infection tropism and dynamics in human microglia, demonstrating the susceptibility of microglia to both clinical and laboratory HCMV strains, albeit with lower efficacy for the laboratory strain, implying that both the gH/gL-trimer and -pentamer can mediate virus entry in microglia. The importance of the gH/gL pentamer for virus entry was demonstrated by the inhibition of virus infection upon pre-incubation with a soluble neuropilin-2 (NRP-2) entry factor. Further, we demonstrated that HCMV infection can be effectively inhibited by monoclonal antibodies specific for the gH/gL complexes and HCMV hyperimmunoglobulin. Lastly, we report that microglia infection can be prevented by newly characterized chemical entry inhibitors. Altogether, these findings underscore the potential of microglia as valuable models for studying HCMV neurotropism and strategies to block virus infection in cells that can impact neurological disorders.
Keywords: tropism; antibodies; entry inhibitors; human cytomegalovirus; microglia; neuropilin-2 (NRP-2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

