Spatial Heterogeneity, Stromal Phenotypes, and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Colorectal Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis
- PMID: 40299767
- PMCID: PMC12163601
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-3780
Spatial Heterogeneity, Stromal Phenotypes, and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Colorectal Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis
Abstract
Purpose: Peritoneal metastases (PM) in colorectal cancer portend a poor prognosis. We sought to elucidate molecular features differentiating primary tumors (PT) from PMs and actionable targets facilitating transcoelomic dissemination and progression.
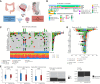
Experimental design: We performed multiomic profiling of 227 samples from 136 patients, including 56 PTs and 120 synchronous PMs comprising 34 matched PT-PM pairs. Whole-exome and bulk RNA sequencing analyses were conducted to identify underlying genomic aberrations and transcriptomic differences between primary and peritoneal lesions. We spatially characterized the microenvironment of tumor-stroma compartments and studied the roles of stromal phenotypes in promulgating tumorigenesis.
Results: Whole-exome sequencing found that genomic alterations and clonality patterns between PTs and PMs remain broadly similar. Transcriptomic profiles, however, suggest a transition as tumors reach the peritoneum toward a more mesenchymal tumor profile and fibrotic tumor microenvironment. Applying spatial profiling, we identify a fibro-collagenous and immune-infiltrated stromal phenotype [stromal cluster (SC) 2] characterized by increased cancer-associated fibroblasts, memory B cells, M2 macrophages, and T-cell exhaustion. These findings were orthogonally validated by multiplex IHC. Patients with SC2 stroma had poorer survival and were characterized by high SERPINE-1 (PAI-1) expression. PMs in patients with SC2 stroma were associated with enriched oncogenic pathways such as TGF-β. PAI-1 inhibition of colorectal cancer PM cell lines with a novel biologic demonstrated reduced IL2-STAT5 and TGF-β pathways and cell death.
Conclusions: Our findings unveil distinctive and actionable molecular signatures, offering deeper insights into the intricate cross-talk between tumor cells and stromal microenvironments enabling PM in colorectal cancer.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.-A.J. Ong reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. J.J. Zhao reports grants from National University Health System Seed Fund (NUHSRO/2024/008/RO5+6/Seed-Sep23/01), National University Hospital Junior Research Award 2023 (JRA/Sep23/002), Chan Heng Leong Education & Research Fund 2024 Award by the National University Hospital Singapore, 2025 Conquer Cancer Merit Award by Conquer Cancer, the ASCO Foundation, and Dean’s Research Development Award awarded by the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, during the conduct of the study. Y. Liu reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. Q.X. Tan reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. J.W.S. Tan reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. J.-Y.J. Lee reports personal fees from National University Hospital (consultant) during the conduct of the study, as well as ImmunoQs (co-founder and COO). L.-H. Loo reports personal fees from National University Hospital (consultant) during the conduct of the study, as well as ImmunoQs (co-founder and CEO). C.Y.L. Chong reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. W. Guo reports a patent for 10202401700P pending. R.Y.K. Tay reports grants from the Clinician Scientist Development Unit (CSDU) NUS Medicine Student Research Mentorship Program. R. Walsh reports personal fees from Pfizer, Novartis, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Daiichi Sankyo outside the submitted work. F. Morano reports personal fees from Pierre Fabre, Servier, and Accademia della Medicina, non-financial support from Pierre Fabre, Amgen, and AstraZeneca, and grants from Incyte outside the submitted work. L. Vermeulen reports employment with Genentech Inc. and ownership of Roche shares. M.F. Bijlsma reports grants from Celgene, Frame Therapeutics, Lead Pharma, and Wholomics and personal fees from Servier and Olympus outside the submitted work. S.J. Klempner reports personal fees from Astellas, Amgen, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Elevation Oncology, Taiho, Gilead Sciences, BeiGene, Eisai, Natera, Sanofi-Aventis, Mersana, and I-Mab outside the submitted work. F. Pietrantonio reports grants from Amgen, Agenus, Eli Lilly and Company, AstraZeneca, Rottapharm, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Incyte and personal fees from BeiGene, Agenus, Gilead Sciences, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, AstraZeneca, Servier, Merck-Serono, Amgen, Bayer, Takeda, Pierre Fabre, Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Jazz, Incyte, Astellas, Pfizer, and Italfarmaco outside the submitted work. R. Sundar reports grants from National Medical Research Council during the conduct of the study; personal fees and other support from Astellas, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, DKSH, Ipsen, MSD, Roche, Taiho, and Teladoc; other support from Auristone, Bayer, CytoMed, Eisai, GSK, Merck, Natera, Novartis, Paxman Coolers, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, and Tavotek BioTherapeutics; and personal fees from Eli Lilly and Company outside the submitted work; in addition, R. Sundar reports a patent for Auristone pending and a patent for Paxman Coolers pending. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures





References
-
- Franko J, Shi Q, Meyers JP, Maughan TS, Adams RA, Seymour MT, et al. Prognosis of patients with peritoneal metastatic colorectal cancer given systemic therapy: an analysis of individual patient data from prospective randomised trials from the Analysis and Research in Cancers of the Digestive System (ARCAD) database. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:1709–19. - PubMed
-
- Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2016;16:582–98. - PubMed
-
- Monteran L, Zait Y, Erez N. It’s all about the base: stromal cells are central orchestrators of metastasis. Trends Cancer 2024;10:208–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOH-000967/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- MOH-CIRG24jan-0044/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- JRA/Sep23/002/National University Health System (NUHS)
- MOH-OFLCG23-may0031/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- A*STAR I&E GAP Fund (I24D1AG082)/Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
- NMRC/MOH-000627/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- MOH-OFYIRG24jan-0052/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- Industry Alignment Fund-Industry Collaboration Fund (IAF-ICP I2201E0014)/Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
- A*STAR Biomedical Engineering Programme (C211318003)/Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
- OFYIRG19may-0007/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- MOH-CSAINV22jul-0005/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- Dean's Research Development Award/National University of Singapore (NUS)
- MOH-OFLCG18May-0003/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- MOH-CIRG21jun-0005/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- MOH-000323-00/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- NUHSRO/2024/008/RO5+6/Seed-Sep23/01/National University Health System (NUHS)
- NMRC/CIRG23Jul-0035/National Medical Research Council (NMRC)
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

