Preclinical Activity of Datopotamab Deruxtecan, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting Trophoblast Cell-Surface Antigen 2, in Uterine Serous Carcinoma
- PMID: 40299780
- PMCID: PMC12062949
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-25-0057
Preclinical Activity of Datopotamab Deruxtecan, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting Trophoblast Cell-Surface Antigen 2, in Uterine Serous Carcinoma
Abstract
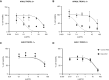
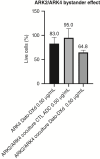
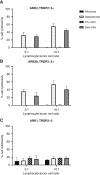
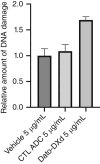
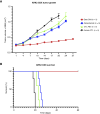
Uterine serous carcinoma (USC) is a rare subset of endometrial cancer with a poor prognosis and high recurrence rate. Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) is a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). The objective of this study was to evaluate the preclinical activity of Dato-DXd in USC in vitro against primary USC cell lines with various trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2) expression and in vivo in TROP2-overexpressing cell line-derived mice xenografts. USC primary tumor cell lines were treated with Dato-DXd and a control ADC (CTL ADC) to evaluate cell viability following exposure. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against TROP2-overexpressing and -nonexpressing cell lines was evaluated using a 4-hour chromium release assay. USC xenografts in mice were treated with Dato-DXd, CTL ADC, datopotamab, and vehicle to assess the in vivo effects via retro-orbital Dato-DXd administration. We found USC cell lines with TROP2 overexpression to be significantly more sensitive to killing induced by Dato-DXd compared with CTL ADC in vitro (e.g., IC50: 0.11 µmol/L vs. 30.07 µmol/L, P = 0.0074 and 0.11 µmol/L vs. 48.95 µmol/L, P = 0.0127, respectively). Dato-DXd induced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the presence of peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy donors. TROP2-nonexpressing cell lines demonstrated minimal killing by Dato-DXd; however, when admixed with TROP2-overexpressing cells, a significant bystander effect was appreciated. In vivo, mice xenografts overexpressing TROP2 treated with Dato-DXd demonstrated tumor growth suppression and longer overall survival compared with CTL ADC-treated xenografts. These data demonstrate Dato-DXd to be highly active against TROP2-overexpressing USC in vitro and in vivo. Our preclinical activity results warrant future clinical trials for patients with advanced or recurrent USC.
Significance: Targeted treatment of USC using the biomarker TROP2 represents a significant opportunity for further treatment options for patients already resistant to other lines of treatment. In this study, we present data showing preclinical evidence of effectiveness of this biomarker-targeted therapy in USC.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D. Santin reports grants and personal fees from Gilead Sciences, R Pharm US, Daiichi Sankyo, and Merck and grants from Verastem Oncology outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preclinical activity of datopotamab deruxtecan, a novel TROP2 directed antibody-drug conjugate targeting trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2) in ovarian carcinoma.Gynecol Oncol. 2024 Oct;189:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2024.07.002. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Gynecol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38981151
-
Datopotamab deruxtecan, a novel TROP2-tareting antibody-drug conjugate with a topoisomerase I inhibitor payload, shows preclinical activity against primary and metastatic uterine and ovarian TROP2 over-expressing carcinosarcoma.Gynecol Oncol. 2025 Jun 28;199:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2025.06.017. Online ahead of print. Gynecol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40582040
-
In vitro and in vivo activity of sacituzumab govitecan, an antibody-drug conjugate targeting trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (Trop-2) in uterine serous carcinoma.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Feb;156(2):430-438. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2019.11.018. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31839338
-
Therapeutic Potential of Datopotamab Deruxtecan in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence to Date.Onco Targets Ther. 2025 Apr 23;18:575-584. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S466220. eCollection 2025. Onco Targets Ther. 2025. PMID: 40291609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An evaluation of datopotamab deruxtecan for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2025 Jul;25(7):695-701. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2025.2519532. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40515573 Review.
References
-
- SEER, National Cancer Institute . Cancer stat facts: uterine cancer. 2022.
-
- Ferriss JS, Erickson BK, Shih IM, Fader AN. Uterine serous carcinoma: key advances and novel treatment approaches. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2021;31:1165–74. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Rustum N, Yashar C, Arend R, Barber E, Bradley K, Brooks R, et al. . Uterine neoplasms, version 1.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2023;21:181–209. - PubMed
-
- Khongorzul P, Ling CJ, Khan FU, Ihsan AU, Zhang J. Antibody-drug conjugates: a comprehensive review. Mol Cancer Res 2020;18:3–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

