Noninvasive Hemodynamic Assessment by a Sensor Patch: The PATCHWRK (PortAble TeCHnology for Wireless caRdiomyopathy tracKing) Study
- PMID: 40300304
- PMCID: PMC12242580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101753
Noninvasive Hemodynamic Assessment by a Sensor Patch: The PATCHWRK (PortAble TeCHnology for Wireless caRdiomyopathy tracKing) Study
Abstract
Background: Echocardiographic timing intervals provide prognostic information in patients with preclinical cardiac dysfunction. Reduced diastolic filling time (DFT) identifies left bundle branch block patients at risk for cardiomyopathy. The need for specialized equipment limits the utility of echocardiography (echo) for longitudinal assessment.
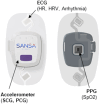
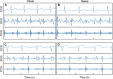
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate a multimodal sensor patch's (SANSA) assessment of DFT, pre-ejection period (PEP), and left ventricular ejection time (LVET).
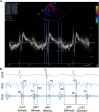
Methods: Fifty patients undergoing echo were prospectively enrolled and had simultaneous SANSA patch recording and echo. Timing intervals were analyzed using continuous wave, pulsed wave, and tissue Doppler imaging. SANSA electrocardiogram, seismocardiogram, and phonocardiogram data were independently analyzed to identify valve openings/closures for DFT, PEP, and LVET estimation. Agreement between echo and SANSA estimates was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and compared with agreement between echo views.
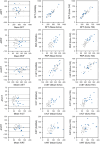
Results: Forty-six of the 50 patients (92%) had analyzable data. The mean ejection fraction was 53% ± 8%; 13 patients (26%) had left bundle branch block. Echo-estimated mean DFT, PEP, and LVET were 416 ± 139 milliseconds (ms), 108 ± 32 ms, and 300 ± 36 ms, respectively. SANSA-estimated DFT, PEP, and LVET were 431 ± 135 ms, 91 ± 35 ms, and 285 ± 43 ms, respectively. The ICC for SANSA vs echo was 0.92 for DFT, 0.74 for PEP, and 0.76 for LVET. The ICC for tissue Doppler imaging vs pulsed wave estimates within the same patients was 0.93 for DFT, 0.83 for PEP, and 0.69 for LVET.
Conclusions: SANSA patch monitoring accurately measures key cardiac timing intervals to within the variability observed between echo views. As these intervals have prognostic value, SANSA-based longitudinal monitoring may facilitate early cardiomyopathy detection.
Keywords: diastolic function; echocardiography; left bundle branch block; patch sensor.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding support and author disclosures This work was funded by NIH grant 1R43HL158282. Dr Loring has received grant support from Boston Scientific and the Department of Veterans Affairs and has served as a consultant for Huxley Medical Inc and Boston Scientific. Dr Piccini is supported by R01AG074185 from the National Institutes of Aging; has received grants for clinical research from Abbott, the American Heart Association, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, iRhythm, and Philips; and also has served as a consultant to Abbott, Abbvie, Ablacon, Altathera, ARCA Biopharma, Bayer, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb (Myokardia), Element Science, Huxley Medical Inc, Itamar Medical, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, ElectroPhysiology Frontiers, ReCor, Sanofi, Philips, and Up-to-Date. Dr Atwater has received research support from Medtronic and Pfizer and has served as a consultant to Medtronic, Biosense Webster, and Cortex Medical. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between Left Ventricular Geometry, Systolic Ejection Time, and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Ambulatory Patients with Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction.Cardiology. 2024 Oct 1:1-11. doi: 10.1159/000541725. Online ahead of print. Cardiology. 2024. PMID: 39353411
-
Lower left ventricular ejection time in MYBPC3 variant carriers with overt or subclinical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Jul 4. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15346. Online ahead of print. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40613316
-
Variation within and between digital pathology and light microscopy for the diagnosis of histopathology slides: blinded crossover comparison study.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jul;29(30):1-75. doi: 10.3310/SPLK4325. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40654002 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost-utility for these groups in a UK context.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(27):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-164. doi: 10.3310/hta10270. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904046
References
-
- Wang N.C., Singh M., Adelstein E.C., et al. New-onset left bundle branch block-associated idiopathic nonischemic cardiomyopathy and left ventricular ejection fraction response to guideline-directed therapies: the NEOLITH study. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13(4):933–942. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

