Impact of ER stress and the unfolded protein response on Fabry disease
- PMID: 40300326
- PMCID: PMC12242609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105733
Impact of ER stress and the unfolded protein response on Fabry disease
Abstract
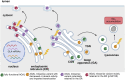
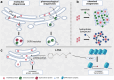
Fabry disease (FD) is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by pathogenic missense and nonsense variants in the α-galactosidase A (GLA) gene, leading to absent or reduced enzyme activity. The resulting lysosomal accumulation of the substrate globotriaosylceramide leads to progressive renal failure, cardiomyopathy with (malignant) cardiac arrhythmias and progressive heart failure as well as recurrent strokes, which significantly limits the life expectancy of patients affected with FD. There is increasing evidence that pathogenic GLA missense variants as well as formally benign GLA variants can cause retention in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), resulting in ER stress, which in turn triggers an unfolded protein response (UPR) leading to cellular dysregulation including inflammation, irreversible cell damage, and apoptosis. This review aims to provide an update on the pathogenetic significance of ER stress and UPR in FD, current treatment options, including pharmaceutical and chemical chaperones, and an outlook on current research and future treatment options in FD.
Keywords: Chaperones; Lysosomal storage disorder; Missense variants.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Malte Lenders received research/travel grants and/or speaker honoraria from Amicus Therapeutics, Sanofi, Chiesi, Sumitomo Pharma, and Takeda. Eva Brand received research grants and/or speaker honoraria from Amicus Therapeutics, Sanofi, Chiesi, Takeda, and Eleva. Elisa Rudolph has nothing to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Schubert U., Antón L.C., Gibbs J., Norbury C.C., Yewdell J.W., Bennink J.R. Rapid degradation of a large fraction of newly synthesized proteins by proteasomes. Nature. 2000;404:770–774. - PubMed
-
- Feriozzi S., Rozenfeld P. Pathology and pathogenic pathways in fabry nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021;25:925–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

