The Epidemiology of Huntington's Disease in Iceland
- PMID: 40300581
- PMCID: PMC12162110
- DOI: 10.1159/000546150
The Epidemiology of Huntington's Disease in Iceland
Abstract
<p>Introduction: Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by involuntary movements, psychiatric symptoms and cognitive decline. Its prevalence is highest in individuals of European descent. However, a previous study in 2007 in Iceland showed an unusually low incidence and prevalence. The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence and prevalence of HD in Iceland between 2008 and 2022 as well as age, sex, symptoms, number of cytidine-adenosine-guanosine (CAG) repeats, treatment, and prognosis.
Methods: A retrospective epidemiological study was conducted with clinical information obtained from medical records of individuals diagnosed with HD 2008-2022. Information was also obtained from the Department of Genetics at University Hospital of Iceland and neurologists managing HD patients.
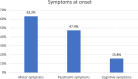
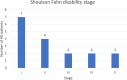
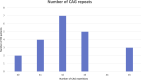
Results: Among the 22 diagnosed individuals (11 men) identified, the point prevalence on December 31, 2022, was 4.38 per 100,000 inhabitants, with an average annual incidence rate of 0.314 per 100,000 person-years. The average age at symptom onset was 46.3 years. A total of 21 out of 22 individuals had confirmed HD through genetic testing, with an average CAG repeat length of 42.3 (range 40-45). Five individuals died during the study period, with the most common cause of death being aspiration pneumonia. The average age at death was 70.4 years.
Conclusion: The prevalence and incidence of HD in Iceland have increased compared to the 2007 study but remain lower than in other European populations. Results showed a lower number of CAG repeats in the Icelandic HD population, potentially explaining the higher age at symptom onset and death compared to global averages. </p>.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant; Huntington’s disease; Iceland; Incidence; Prevalence.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Incidence of adult Huntington's disease in the UK: a UK-based primary care study and a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2016 Feb 23;6(2):e009070. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009070. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 26908513 Free PMC article.
-
Huntington's Disease in Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Brazil: Three-Year Update.Neurodegener Dis. 2025;25(2):88-105. doi: 10.1159/000538170. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Neurodegener Dis. 2025. PMID: 39978329
-
Therapeutic strategies for Huntington's disease: current approaches and future direction.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2025 Aug 28:1-15. doi: 10.1080/17582024.2025.2552593. Online ahead of print. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2025. PMID: 40874597 Review.
-
[Cervical artery dissection in Iceland: epidemiology, treatment and prognosis].Laeknabladid. 2024 Nov;110(11):506-511. doi: 10.17992/lbl.2024.11.812. Laeknabladid. 2024. PMID: 40801908 Icelandic.
References
-
- Martin JB, Gusella JF. Huntington’s disease: pathogenesis and management. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(20):1267–76. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh R, Tabrizi SJ. Huntington disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;147:255–78. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald M. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell. 1993;72(6):971–83. - PubMed
-
- Fisher ER, Hayden MR. Multisource ascertainment of Huntington disease in Canada: prevalence and population at risk. Mov Disord. 2014;29(1):105–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical