Vascular remodeling in arteriovenous fistula treated with PDE5A inhibitors
- PMID: 40300852
- PMCID: PMC12040441
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70331
Vascular remodeling in arteriovenous fistula treated with PDE5A inhibitors
Abstract
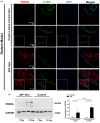
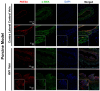
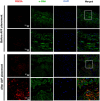
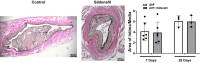
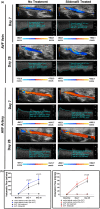
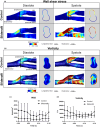
The arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is the lifeline for hemodialysis patients. However, there are currently no effective therapies promoting AVF maturation. AVF dilation by smooth muscle cell relaxation, through increased cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), is one potential mechanism to improve AVF remodeling. In this study, we examined the cGMP pathway and its inhibitor phosphodiesterase 5A (PDE5A) in rat, pig, and human AVF. We administered the PDE5A inhibitor, sildenafil, to rats with femoral AVFs and analyzed AVF histological and hemodynamic parameters. We observed that AVF creation increases PDE5A expression in rodent and porcine AVF models. Similarly, we observed an increase in PDE5A expression in the anastomotic regions of AVFs from hemodialysis patients when compared to pre-AVF placement. Sildenafil-treated rats showed significantly increased ultrasound-derived AVF volumetric blood flow and increased MRI-derived 3-dimensional lumen diameter when compared to controls. MRI-based computational fluid dynamics showed that sildenafil-treated rats had increased anastomotic hemodynamics compared to control rats. Histology showed similar intimal hyperplasia in sildenafil-treated and control rats. In conclusion, sildenafil treatment increases AVF vein outward expansion and blood flow without affecting the level of intimal hyperplasia. PDE5A inhibitors serve as a potential therapeutic approach to promote AVF maturation by enhancing outward vascular remodeling.
Keywords: PDE5A; arteriovenous fistula; hemodialysis; sildenafil; vascular access; vascular remodeling.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Timmy Lee is a consultant for BD Bard, Boston Scientific, Xeltis, and Venostent. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollahi, M. , Fooladian, F. , Emami, B. , Zafari, K. , & Bahreini‐Moghadam, A. (2003). Protection by sildenafil and theophylline of lead acetate‐induced oxidative stress in rat submandibular gland and saliva. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 22, 587–592. - PubMed
-
- Alsaadi, M. J. (2022). Arteriovenous fistula anastomosis diameter association with the ischemic steal syndrome occurrence. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 10, 2621–2626.
-
- Birschmann, I. , & Walter, U. (2004). Physiology and pathophysiology of vascular signaling controlled by guanosine 3′,5′‐cyclic monophosphate‐dependent protein kinase. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 51, 397–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

