Selective BCL-2 inhibitor triggers STING-dependent antitumor immunity via inducing mtDNA release
- PMID: 40300857
- PMCID: PMC12056644
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010889
Selective BCL-2 inhibitor triggers STING-dependent antitumor immunity via inducing mtDNA release
Abstract
Background: The stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway has been demonstrated to propagate the cancer-immunity cycle and remodel the tumor microenvironment and has emerged as an appealing target for cancer immunotherapy. Interest in STING agonist development has increased, and the candidates hold significant promise; however, most are still in the early stages of human clinical trials. We found that ABT-199 activated the STING pathway to enhance the immunotherapeutic effect, and provided a ready-to-use small molecule drug for STING signaling activation.
Methods: Phosphorylation of STING, TBK1, and IRF3, as well as activation of the interferon-I (IFN-I) signaling pathway, were detected following ABT-199 treatment in various colorectal cancer cells. C57BL/6J and BALB/c mice with subcutaneous tumors were employed to evaluate the in vivo therapeutic effects of the ABT-199 and anti-PD-L1 combination. Flow cytometry and ELISA were employed to analyze the level and activity of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes. Immunofluorescence and quantitative real-time PCR were conducted to assess the source and accumulation of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the cytoplasm. Chemical cross-linking assay, co-immunoprecipitation, and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout were performed to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying ABT-199-induced voltage-dependent anion channel protein 1 (VDAC1) oligomerization and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) release.
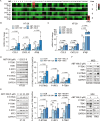
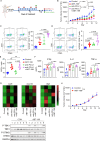
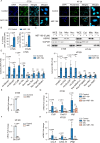
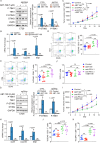
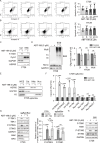
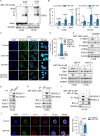
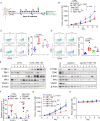
Results: ABT-199 significantly activated the STING signaling pathway in various colorectal cancer cells, which was evidenced by increased phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3, and upregulation of C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10), and interferon beta transcription. By promoting chemokine expression and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration, ABT-199 promoted antitumor immunity and synergized with anti-PD-L1 therapy to improve antitumor efficacy. ABT-199 induced mtDNA accumulation in the cytoplasm and triggered STING signaling via the canonical pathway. cGAS or STING-KO models significantly abolished both STING signaling activation and the antitumor efficacy of ABT-199. Mechanically, ABT-199 promoted VDAC1 oligomerization by disturbing the binding between BCL-2 and VDAC1, thereby facilitating mtDNA release into the cytoplasm. ABT-199-triggered STING signaling was attenuated when VADC1 was knocked out. Consistently, the antitumor effect of ABT-199 in vivo was abolished in the absence of VDAC1.
Conclusions: Our results identify a ready-to-use small molecule compound for STING activation, reveal the underlying molecular mechanism through which ABT-199 activates the STING signaling pathway, and provide a theoretical basis for the use of ABT-199 in cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Colorectal Cancer; Cytokine; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No, there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondria-targeted manganese-based mesoporous silica nanoplatforms trigger cGAS-STING activation and sensitize anti PD-L1 therapy in triple-negative breast cancer.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 1;199:374-386. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.04.040. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40294811
-
Rocaglamide promotes the infiltration and antitumor immunity of NK cells by activating cGAS-STING signaling in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):585-598. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.65019. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002511 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation Therapy Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Cloaking via PD-L1 Upregulation Induced by cGAS-STING Activation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Apr 1;112(5):1243-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.12.162. Epub 2022 Jan 2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 34986380
-
Strategies involving STING pathway activation for cancer immunotherapy: Mechanism and agonists.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jul;213:115596. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115596. Epub 2023 May 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37201875 Review.
-
Advances in nanoplatform-based multimodal combination therapy activating STING pathway for enhanced anti-tumor immunotherapy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Jun;250:114573. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114573. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 39983453 Review.
Cited by
-
cGAS-STING pathway as a promising target for digestive diseases: insights from natural plant products.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 20;12:1594120. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1594120. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40621423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
