Multifaceted role of nitric oxide in vascular dementia
- PMID: 40300885
- PMCID: PMC12124705
- DOI: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00158
Multifaceted role of nitric oxide in vascular dementia
Abstract
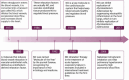
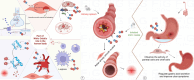
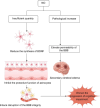
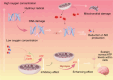
Vascular dementia is a highly heterogeneous neurodegenerative disorder induced by a variety of factors. Currently, there are no definitive treatments for the cognitive dysfunction associated with vascular dementia. However, early detection and preventive measures have proven effective in reducing the risk of onset and improving patient prognosis. Nitric oxide plays an integral role in various physiological and pathological processes within the central nervous system. In recent years, nitric oxide has been implicated in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and has emerged as a crucial factor in the pathophysiology of vascular dementia. At different stages of vascular dementia, nitric oxide levels and bioavailability undergo dynamic alterations, with a marked reduction in the later stages, which significantly contributes to the cognitive deficits associated with the disease. This review provides a comprehensive review of the emerging role of nitric oxide in the physiological and pathological processes underlying vascular dementia, focusing on its effects on synaptic dysfunction, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and blood‒brain barrier integrity. Furthermore, we suggest that targeting the nitric oxide soluble guanylate cyclase-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway through specific therapeutic strategies may offer a novel approach for treating vascular dementia, potentially improving both cognitive function and patient prognosis. The review contributes to a better understanding of the multifaceted role of nitric oxide in vascular dementia and to offering insights into future therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: apoptosis; blood‒brain barrier; cell death; dementia; mitochondrial dysfunction; neuroprotection; nitric oxide; nitric oxide synthase; oxidative stress; vascular dementia.
Copyright © 2025 Medical Gas Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The emerging role of nitric oxide in the synaptic dysfunction of vascular dementia.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Feb 1;20(2):402-415. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01353. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38819044 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Nitric Oxide Synthase/Nitric Oxide Pathway in the Pathology of Vascular Dementia and Related Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 26;22(9):4540. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094540. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33926146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and its interaction with soluble guanylate cyclase is a key factor for the vascular dysfunction of experimental sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun;42(6):e391-400. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000301. Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24717470 Clinical Trial.
-
Inhaled nitric oxide decreases pulmonary soluble guanylate cyclase protein levels in 1-month-old lambs.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004 May;127(5):1285-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.07.024. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004. PMID: 15115984
-
Vascular oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease.J Neurol Sci. 2007 Jun 15;257(1-2):240-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.01.039. Epub 2007 Mar 6. J Neurol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17337008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

