Deep learning based automated left atrial segmentation and flow quantification of real time phase contrast MRI in patients with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 40301204
- PMCID: PMC12162695
- DOI: 10.1007/s10554-025-03407-9
Deep learning based automated left atrial segmentation and flow quantification of real time phase contrast MRI in patients with atrial fibrillation
Abstract
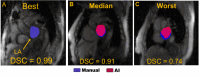
Real time 2D phase contrast (RTPC) MRI is useful for flow quantification in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients, but data analysis requires time-consuming anatomical contouring for many cardiac time frames. Our goal was to develop a convolutional neural network (CNN) for fully automated left atrial (LA) flow quantification. Forty-four AF patients underwent cardiac MRI including LA RTPC, collecting a median of 358 timeframes per scan. 15,307 semi-manual derived RTPC LA contours comprised ground truth for CNN training, validation, and testing. CNN vs. human performance was assessed using Dice scores (DSC), Hausdorff distance (HD), and flow measures (stasis, velocities, flow). LA contour DSC across all patients were similar to human inter-observer DSC (0.90 vs. 0.93) and a median 4.6 mm [3.5-5.9 mm] HD. There was no impact of heart rate variability on contouring quality (low vs. high variability DSC: 0.92 ± 0.05 vs. 0.91 ± 0.03, p = 0.95). CNN based LA flow quantification showed good to excellent agreement with semi-manual analysis (r > 0.90) and small bias in Bland-Altman analysis for mean velocity (-0.10 cm/s), stasis (1%), and net flow (-2.4 ml/s). This study demonstrated the feasibility of CNN based LA flow analysis with good agreements in LA contours and flow measures and resilience to heartbeat variability in AF.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; Deep learning; Image processing; Real time phase contrast.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Left atrial 4D flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a reproducibility study in sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 Mar 22;23(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00729-0. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33745457 Free PMC article.
-
Automated left atrial time-resolved segmentation in MRI long-axis cine images using active contours.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Jun 19;21(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00630-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34147081 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Beat-To-Beat Variability in Left Atrial Hemodynamics Using Real Time Phase Contrast MRI in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Sep;58(3):763-771. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28550. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36468562 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of left and right atrial 3D hemodynamics in patients with atrial fibrillation: a 4D flow MRI study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 May;32(5):807-15. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0830-8. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26820740
-
Left Atrial and Left Atrial Appendage 4D Blood Flow Dynamics in Atrial Fibrillation.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Sep;9(9):e004984. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.004984. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27613699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gatehouse PD et al (2005) Applications of phase-contrast flow and velocity imaging in cardiovascular MRI. European Radiology vol. 15 2172–2184 Preprint at 10.1007/s00330-005-2829-3 - PubMed
-
- Srichai MB, Lim RP, Wong S, Lee VS (2009) Cardiovascular applications of Phase-Contrast MRI. Am J Roentgenol 192:662–675 - PubMed
-
- Powell AJ, Geva T (2000) Blood flow measurement by magnetic resonance imaging in congenital heart disease. Pediatric Cardiology vol. 21 47–58 Preprint at 10.1007/s002469910007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

