Epitope-optimized vaccine elicits enduring immunity against swine influenza A virus
- PMID: 40301303
- PMCID: PMC12041224
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59182-7
Epitope-optimized vaccine elicits enduring immunity against swine influenza A virus
Abstract
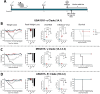
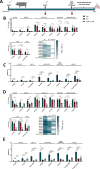
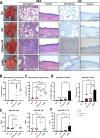
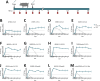
Swine Influenza A Virus (IAV-S) poses a significant burden to both the pork industry and public health. Current vaccines against IAV-S are infrequently updated and induce strain-specific immunity. Computational platforms have recently emerged as a promising strategy to develop new-age vaccines. Here, we describe the Epigraph, a computationally derived and epitope optimized set of vaccine immunogens. When compared to wildtype immunogens (WT) and a commercial comparator (FluSure XP®), pigs immunized with Epigraph demonstrate significantly improved breadth and magnitude of antibody responses. Further, pigs immunized with Epigraph show more robust and a wider breadth of cross-reactive cell-mediated immune responses than pigs immunized with WT immunogens. In an experimental infection model, Epigraph immunized pigs demonstrate a significant reduction of clinical disease, lower shedding of infectious virus, reduction of lung lesions, and lower microscopic immunopathology compared to the other immunization groups. These data support the continued investigation of computationally designed and epitope optimized vaccine immunogens against influenza A virus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: E.A.W. is an inventor of the Epigraph immunogens in this study and has a patent application in progress (Application: 62/734,791; International Application: PCT/US19/52137). Due to patents and pending applications restrictions apply regarding the public availability of sequence information for the reported immunogens. However, unique biologicals and sequence information can be requested at Nutech Ventures, Lincoln, NE (US) by contacting info@nutechventures.org and will be processed as promptly as possible. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI147109/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 AI125207/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI125207/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AI147109/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2020-06448/United States Department of Agriculture | Agricultural Research Service (USDA Agricultural Research Service)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

