Acetylated KIAA1429 by TIP60 facilitates metastasis and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via N6-methyladenosine-KDM5B-mediated regulation of FoxO1
- PMID: 40301310
- PMCID: PMC12041376
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02462-4
Acetylated KIAA1429 by TIP60 facilitates metastasis and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via N6-methyladenosine-KDM5B-mediated regulation of FoxO1
Abstract
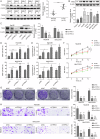
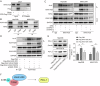
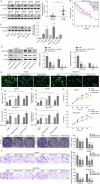
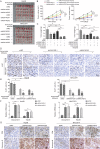
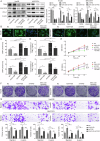
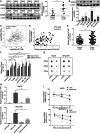
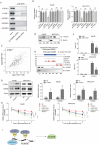
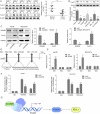
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is characterized by programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1)-mediated immune escape. This study aimed to elucidate the function and mechanism behind KIAA1429, a component of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) complex, in immune escape of HCC. PD-L1 expression was assessed through immunofluorescence staining, and flow cytometry was used to determine CD8+ T cell percentage. The level of IFN-γ was detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were evaluated through CCK-8, colony formation, and Transwell assays, respectively. The m6A modification level was measured using an RNA methylation quantification assay, m6A dot blot, and methylated RNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR. Molecule interaction was validated using RNA pulldown, RNA immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and co-immunoprecipitation assays. In vivo HCC growth was evaluated in NOD/SCID mice. We found that TIP60, KIAA1429 and KDM5B were highly expressed in HCC cells, while FoxO1 was poorly expressed. Functionally, TIP60/KIAA1429 silencing inhibited PD-L1-mediated HCC immune evasion, growth, migration, and invasion. Mechanistically, TIP60 led to acetylation of KIAA1429, which promoted KDM5B expression in an m6A-YTHDF1-dependent manner, and subsequently restrained the transcription and expression of FoxO1. Enforcing YTHDF1 expression or depleting FoxO1 expression markedly reversed the suppressive effect of shKIAA1429 on HCC immune evasion, growth, migration, and invasion. Overall, these findings suggest that acetylated KIAA1429-mediated m6A modification endows HCC cells with immune evasion through regulation of KDM5B/FoxO1 axis, which provide a treatment option for HCC by targeting KIAA1429.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SYVN1 ubiquitinates FoxO1 to induce β-catenin nuclear translocation, PD-L1-mediated metastasis, and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Oct;46(5):1285-1299. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00811-y. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 37099251 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the KIAA1429/KLF1/PD-L1 Axis in Regulating Immune Escape in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):1835-1845. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01592-3. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39499390
-
KIAA1429 regulates the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering m6A modification of ID2 mRNA.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 7;12:3421-3428. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S180954. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118692 Free PMC article.
-
KIAA1429-mediated RXFP1 attenuates non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis via N6-methyladenosine modification.Cancer Biomark. 2024 Feb 7:CBM230188. doi: 10.3233/CBM-230188. Online ahead of print. Cancer Biomark. 2024. PMID: 38427468
-
N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase Component KIAA1429 Is a Potential Target of Cancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 17;14(10):1319. doi: 10.3390/biom14101319. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki T, Honjo T. PD-1 and PD-1 ligands: from discovery to clinical application. Int Immunol. 2007;19:813–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

