Immunotherapy for autoimmune encephalitis
- PMID: 40301313
- PMCID: PMC12041578
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02459-z
Immunotherapy for autoimmune encephalitis
Abstract
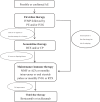
Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is increasingly recognized as a cause of brain disorders that greatly benefit from immunotherapy. Starting treatment quickly and increasing the use of immunotherapy can lead to better results for AE patients. Currently, there are standardized treatment guidelines for treating AE. First-line therapy includes intravenous corticosteroids, plasma exchange, and intravenous immunoglobulin. Second-line therapy involves rituximab, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine. Third-line therapy uses agents that deplete plasma cells (bortezomib, daratumumab, and obinutuzumab), drugs that modulate cytokines (tocilizumab, anakinra, tofacitinib, and interleukin-2), and treatments that target intrathecal immune cells (intrathecal methotrexate). This review aims to summarize the immunotherapeutic strategies available for treating AE and provide an update on refractory AE.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: Ethics approval was not required for this review article. The analysis is based exclusively on publicly available literature, and the authors did not conduct any original research involving human participants, animal experimentation, or access to private/identifiable data. All studies cited in this review were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of their respective institutions and national regulations.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources