Engineering of extracellular vesicles for efficient intracellular delivery of multimodal therapeutics including genome editors
- PMID: 40301355
- PMCID: PMC12041237
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59377-y
Engineering of extracellular vesicles for efficient intracellular delivery of multimodal therapeutics including genome editors
Abstract
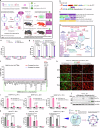
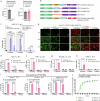
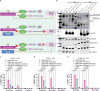
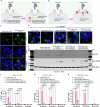
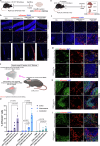
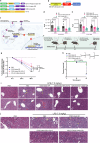
Intracellular delivery of protein and RNA therapeutics represents a major challenge. Here, we develop highly potent engineered extracellular vesicles (EVs) by incorporating bio-inspired attributes required for effective delivery. These comprise an engineered mini-intein protein with self-cleavage activity for active cargo loading and release, and fusogenic VSV-G protein for endosomal escape. Combining these components allows high efficiency recombination and genome editing in vitro following EV-mediated delivery of Cre recombinase and Cas9/sgRNA RNP cargoes, respectively. In vivo, infusion of a single dose Cre loaded EVs into the lateral ventricle in brain of Cre-LoxP R26-LSL-tdTomato reporter mice results in greater than 40% and 30% recombined cells in hippocampus and cortex respectively. In addition, we demonstrate therapeutic potential of this platform by showing inhibition of LPS-induced systemic inflammation via delivery of a super-repressor of NF-ĸB activity. Our data establish these engineered EVs as a platform for effective delivery of multimodal therapeutic cargoes, including for efficient genome editing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: O.W., J.Z. N., D.G. A.G., M.J.A.W. and S.E.-A. are consultants and stakeholders in Evox Therapeutics Limited, Oxford, United Kingdom. A.D.F., and J.H. are employees of Evox Therapeutics Limited, Oxford, United Kingdom. Evox Therapeutics filed a patent application related to the data used in this work. The patent was applied by Evox Therapeutics Limited. The inventors are Xiuming Liang, Dhanu Gupta, Samir EL Andaloussi and Joel Nordin. Its application number is PCT/EP22/84310 which is still under evaluation. The development of VEDIC and VFIC systems of this work was included in this patent. All the data are available in the manuscript or in the supplemental information. Materials are available upon signing the material transfer agreement (MTA) submitted to S.E.-A. and Evox Therapeutics Limited, Oxford, United Kingdom. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Messersmith, W. A. & Ahnen, D. J. Targeting EGFR in Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.359, 1834–1836 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Stewart, M. P. et al. In vitro and ex vivo strategies for intracellular delivery. Nature538, 183–192 (2016). - PubMed
-
- D’Astolfo, D. S. et al. Efficient intracellular delivery of native proteins. Cell161, 674–690 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

