Evolutionary dynamics of behavioral motivations for cooperation
- PMID: 40301382
- PMCID: PMC12041527
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59366-1
Evolutionary dynamics of behavioral motivations for cooperation
Abstract
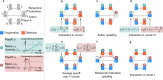
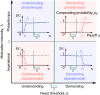
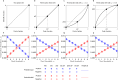
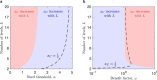
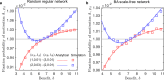
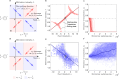
Human decision-making is shaped by underlying motivations, which reflect both subjective well-being and fundamental biological needs. Different needs are often prioritized and traded off against one another. Here we develop a theoretical framework to study the evolution of behavioral motivations, encompassing both philanthropic (cooperating after personal needs are met) and aspirational (cooperating to fulfill personal needs) motivations. Our findings show that when the ratio of benefits to costs for cooperation exceeds a critical threshold, individuals initially driven by aspirational motivations can transition to philanthropic motivations with a low reference point for cooperation, resulting in increased cooperation. Furthermore, the critical threshold depends on the structure of the underlying social network, with network modifications capable of reversing the evolutionary trajectory of motivations. Our results reveal the complex interplay between needs, motivations, social networks, and decision-making, offering insights into how evolution shapes not only cooperative behaviors but also the motivations behind them.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thresholds in the resilience of modular social networks to invasion by defectors.J Theor Biol. 2019 Jan 7;460:56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Oct 6. J Theor Biol. 2019. PMID: 30296450
-
A theory for the evolution of other-regard integrating proximate and ultimate perspectives.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 10;106(45):19061-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904357106. Epub 2009 Oct 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19858492 Free PMC article.
-
Mobility enhances cooperation in the presence of decision-making mistakes on complex networks.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2011 Feb;83(2 Pt 2):026105. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.83.026105. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2011. PMID: 21405887
-
Prosocial primates: selfish and unselfish motivations.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010 Sep 12;365(1553):2711-22. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0119. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20679114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolutionary psychology of climate change behaviors: Insights and applications.Curr Opin Psychol. 2021 Dec;42:54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Curr Opin Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33915462 Review.
References
-
- Darwin, C. On the Origin of Species. (1859).
-
- Hamilton, W. D. The evolution of altruistic behavior. Am. Nat.97, 354–356 (1963).
-
- Trivers, R. L. The evolution of reciprocal altruism. Q. Rev. Biol.46, 35–57 (1971).
-
- Axelrod, R. The Evolution of Cooperation. (New York: Basic Books, 1984).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

