Human-generative AI collaboration enhances task performance but undermines human's intrinsic motivation
- PMID: 40301425
- PMCID: PMC12041296
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98385-2
Human-generative AI collaboration enhances task performance but undermines human's intrinsic motivation
Abstract
In a series of four online experimental studies (total N = 3,562), we investigated the performance augmentation effect and psychological deprivation effect of human-generative AI (GenAI) collaboration in professional settings. Our findings consistently demonstrated that collaboration with GenAI enhanced immediate task performance. However, this performance augmentation effect did not persist in subsequent tasks performed independently by humans. Importantly, transitioning from collaboration with GenAI to solo work led to an increased sense of control of human workers, and was also accompanied by significant decreases in intrinsic motivation and increases in feelings of boredom. These results highlight the complex dual effects of human-GenAI collaboration: It enhances immediate task performance but can undermine long-term psychological experiences of human workers.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



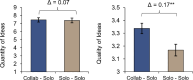



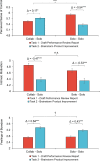
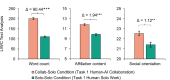




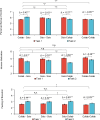
Similar articles
-
An Ethical Perspective on the Democratization of Mental Health With Generative AI.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Oct 17;11:e58011. doi: 10.2196/58011. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39417792 Free PMC article.
-
Promises and challenges of generative artificial intelligence for human learning.Nat Hum Behav. 2024 Oct;8(10):1839-1850. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-02004-5. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Nat Hum Behav. 2024. PMID: 39438686 Review.
-
The First Generative AI Prompt-A-Thon in Healthcare: A Novel Approach to Workforce Engagement with a Private Instance of ChatGPT.PLOS Digit Health. 2024 Jul 23;3(7):e0000394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000394. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLOS Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39042600 Free PMC article.
-
Preconceived beliefs, different reactions: alleviating user switching intentions in service failures through priming GenAI beliefs.BMC Psychol. 2025 May 23;13(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02894-8. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40410923 Free PMC article.
-
Illusion, dilution, or loss: psychological ownership and GenAI.Trends Cogn Sci. 2025 Mar;29(3):215-217. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2024.12.011. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Trends Cogn Sci. 2025. PMID: 39779444 Review.
Cited by
-
The Neurophysiological Paradox of AI-Induced Frustration: A Multimodal Study of Heart Rate Variability, Affective Responses, and Creative Output.Brain Sci. 2025 May 25;15(6):565. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15060565. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40563737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raisch, S. & Krakowski, S. Artificial intelligence and management: the automation–augmentation paradox. Acad. Manag Rev.46, 192–210 (2021).
-
- Wilson, H. J. & Daugherty, P. R. Collaborative intelligence: humans and AI are joining forces. Harv. Bus. Rev.96, 114–123 (2018).
-
- Brynjolfsson, E., Li, D. & Raymond, L. Generative AI at work. Q. J. Econ.140, 889–942 (2025).
-
- Noy, S. & Zhang, W. Experimental evidence on the productivity effects of generative artificial intelligence. Science381, 187–192 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Microsoft AI is already changing work—Microsoft included. Retrieved January 23, from (2025). https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/worklab/ai-is-already-changing-work-micr...
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

