Primary cilia and cancer: a tale of many faces
- PMID: 40301543
- PMCID: PMC12095056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-025-03416-x
Primary cilia and cancer: a tale of many faces
Abstract
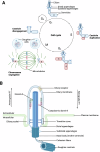
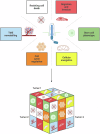
Cilia are microtubule-based sensory organelles which project from the cell surface, enabling detection of mechanical and chemical stimuli from the extracellular environment. It has been shown that cilia are lost in some cancers, while others depend on cilia or ciliary signaling. Several oncogenic molecules, including tyrosine kinases, G-protein coupled receptors, cytosolic kinases, and their downstream effectors localize to cilia. The Hedgehog pathway, one of the most studied ciliary-signaling pathways, is regulated at the cilium via an interplay between Smoothened (an oncogene) and Patched (a tumor suppressor), resulting in the activation of pro-survival programs. Interestingly, cilia loss can result in resistance to Smoothened-targeting drugs and increased cancer cell survival. On the other hand, kinase inhibitor-resistant and chemoresistant cancers have increased cilia and increased Hedgehog pathway activation, and suppressing cilia can overcome this resistance. How cilia regulate cancer is therefore context dependent. Defining the signaling output of cilia-localized oncogenic pathways could identify specific targets for cancer therapy, including the cilium itself. Increasing evidence implicates cilia in supporting several hallmarks of cancer, including migration, invasion, and metabolic rewiring. While cell cycle cues regulate the biogenesis of cilia, the absence of cilia has not been conclusively shown to affect the cell cycle. Thus, a complex interplay between molecular signals, phosphorylation events and spatial regulation renders this fascinating organelle an important new player in cancer through roles that we are only starting to uncover. In this review, we discuss recent advances in our understanding of cilia as signaling platforms in cancer and the influence this plays in tumor development.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

