PYGO2 regulates IL10 and plays immunosuppressive role through ESCC progression
- PMID: 40301712
- PMCID: PMC12038969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-025-00540-0
PYGO2 regulates IL10 and plays immunosuppressive role through ESCC progression
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), one of the most aggressive carcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract, is the sixth most common cause of cancer-related death. Wnt pathway plays a pivotal role in cell proliferation and differentiation. PYGO2 and IL10 are involved in this pathway. Our aim in this study was to examine the correlation between PYGO2 and IL10 expression in ESCC patients and cell lines.
Methods: Relative-comparative real time-PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to evaluate the PYGO2 and IL10 mRNA expression profile in 58 non-treated ESCC compared to their margin normal tissues. Expression of PYGO2 was induced in KYSE-30 and YM1 ESCC lines and IL10 expression was analyzed.
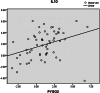
Results: The results revealed the significant overexpression of PYGO2 and IL10 mRNA in 31.0% and 51.7% of ESCCs, respectively. The PYGO2 and IL10 overexpression was significantly correlated to each other (p = 0.007). Concomitant overexpression of the genes was significantly associated to grade of tumor differentiation (p < 0.01), and tumor depth of invasion (p < 0.05). Induced expression of PYGO2 caused a meaningful change in IL10 expression in ESCC cells.
Conclusion: PYGO2 may regulate IL10 through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, suggesting a possible oncogenic role for PYGO2/IL10 axis in ESCC tumorigenesis. Considering the involvement of IL10 as an anti-inflammatory cytokine and PYGO2 role in elevated tumor invasion and metastasis, possible functional interaction between these factors may promote a process which induces invasion and malignant phenotype in ESCC.
Keywords: IL10; PYGO2; Co-overexpression; Quantitative real-time PCR; Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by ethics committee of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (No. 88098) according to the Ethical Helsinki Declaration agreement and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of PYGO2 and EGFR in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2013 Jun;30(2):516. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0516-9. Epub 2013 Mar 3. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23456637
-
NDRG1 overexpression promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through modulating Wnt signaling pathway.Cancer Biol Ther. 2016 Sep;17(9):943-54. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1210734. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27414086 Free PMC article.
-
PYGO2 increases proliferation and migration capacities through critical signaling pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Jan;38(1):e23625. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23625. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38229324
-
lncRNA UCA1 inhibits esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma growth by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2016;79(9-10):407-18. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2016.1176617. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2016. PMID: 27267823
-
Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell cancer.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2646-2652. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14959. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771416
References
-
- Lagergren J, et al. Oesophageal cancer. Lancet. 2017;390(10110):2383–96. - PubMed
-
- Lustig B, Behrens J. The Wnt signaling pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003;129(4):199–221. - PubMed
-
- Mannino MH, et al. The Paradoxical role of IL-10 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;367(2):103–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

