Procalcitonin as a biomarker for postoperative pneumonia: a study on dynamics following cardiopulmonary bypass in adults
- PMID: 40301752
- PMCID: PMC12042508
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-025-04654-3
Procalcitonin as a biomarker for postoperative pneumonia: a study on dynamics following cardiopulmonary bypass in adults
Abstract
Objective: Postoperative pneumonia (POP) frequently complicates cardiac surgery that involves cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). This study aimed to assess the diagnostic utility of procalcitonin (PCT) for identifying pneumonia after CPB-assisted cardiac surgery.
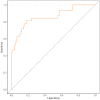
Methods: Patients diagnosed with POP were enrolled in the retrospective matched case-control study and were admitted to a Grade III general hospital in Nanjing in 2023. POP diagnosis was determined based on a combination of clinical and microbiological criteria.PCT and white blood cell count (WBC) data were systematically collected from day 1 (T1) to day 5 (T5). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and subject operating characteristics were utilized to evaluate the diagnostic performance of biomarkers. At the same time, a binary logistic regression model was developed to identify factors that influence the diagnosis of POP.
Results: The study included 220 age- and sex-matched patients, comprising 56 individuals with POP and 164 uninfected patients constituting the non-POP group. ROC curve analysis revealed that serum PCT concentration exhibited an AUC > 0.7 from day 2 to day 5, whereas other indices demonstrated AUCs < 0.7 at these time points. Univariate and multivariate analyses highlighted serum PCT concentration on day 2, WBC count on day 5, the PCTT4-T1 variation rate, and days of mechanical ventilation as significant predictive factors for POP diagnosis, each demonstrating statistical significance (P < 0.05). The calculated AUC was 0.837 (95%CI: 0.773-0.902). The absolute PCT value exhibited superior diagnostic performance relative to its variance rate and WBC count, yielding optimal diagnostic accuracy with a cutoff value of 3.45 ng/ml.
Conclusion: Serum PCT absolute value demonstrates higher sensitivity and specificity than other indices, offering superior diagnostic potential for predicting POP.
Procalcitonin (PCT) levels showed promise as a sensitive and specific marker for predicting postoperative pneumonia (POP) following cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (ethics number: 2024-SR-535). All patients participating in the study signed the informed consent form. Consent for publication: All authors agree to and support the article’s submission and publication. The anonymity of the study will not be compromised by any participants’ images or other personal or clinical details. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kallel S, Abid M, Jarraya A, Abdenadher M, Mnif E, Frikha I, et al. [Kinetics, diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin after cardiac surgery]. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2012;70(5):567–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

